Nucleophagy in Aspergillus oryzae is Mediated by Autophagosome Formation and Vacuole-Mediated Degradation
- PMID: 39162852
- PMCID: PMC11335778
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-024-03838-y
Nucleophagy in Aspergillus oryzae is Mediated by Autophagosome Formation and Vacuole-Mediated Degradation
Abstract
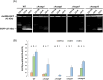
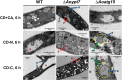
We previously reported autophagy-mediated degradation of nuclei, nucleophagy, in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. In this study, we examined whether nuclei are degraded as a whole. We generated A. oryzae mutants deleted for orthologs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPT7 and ATG15 which are required, respectively, for autophagosome-vacuole fusion and vacuolar degradation of autophagic bodies. Degradation of histone H2B-EGFP under starvation conditions was greatly decreased in the ΔAoypt7 and ΔAoatg15 mutants. Fluorescence and electron microscopic observations showed that autophagosomes and autophagic bodies surrounding the entire nuclei were accumulated in the cytoplasm of ΔAoypt7 and the vacuole of ΔAoatg15, respectively. These results indicate that nuclei are engulfed in the autophagosomes as a whole and transported/released into the vacuolar lumen where they are degraded.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

