Positive feedback loop PU.1-IL9 in Th9 promotes rheumatoid arthritis development
- PMID: 39164066
- PMCID: PMC11672030
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2024-226067
Positive feedback loop PU.1-IL9 in Th9 promotes rheumatoid arthritis development
Abstract
Objectives: T helper 9 (Th9) cells are recognised for their characteristic expression of the transcription factor PU.1 and production of interleukin-9 (IL-9), which has been implicated in various autoimmune diseases. However, its precise relationship with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis needs to be further clarified.
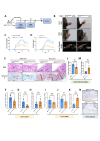
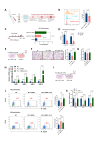
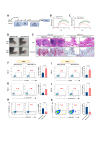
Methods: The expression levels of PU.1 and IL-9 in patients with RA were determined by ELISA, western blotting (WB) and immunohistochemical staining. PU.1-T cell-conditional knockout (KO) mice, IL-9 KO and IL-9R KO mice were used to establish collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA), respectively. The inhibitor of PU.1 and IL-9 blocking antibody was used in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). In an in vitro study, the effects of IL-9 were investigated using siRNAs and IL-9 recombinant proteins. Finally, the underlying mechanisms were further investigated by luciferase reporter analysis, WB and Chip-qPCR.
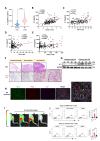
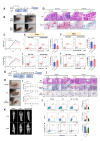
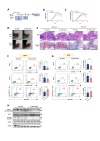
Results: The upregulation of IL-9 expression in patients with RA exhibited a positive correlation with clinical markers. Using CAIA and CIA model, we demonstrated that interventions targeting PU.1 and IL-9 substantially mitigated the inflammatory phenotype. Furthermore, in vitro assays provided the proinflammatory role of IL-9, particularly in the hyperactivation of macrophages and fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mechanistically, we uncovered that PU.1 and IL-9 form a positive feedback loop in RA: (1) PU.1 directly binds to the IL-9 promoter, activating its transcription and (2) Th9-derived IL-9 induces PU.1 via the IL-9R-JAK1/STAT3 pathway.
Conclusions: These results support that the PU.1-IL-9 axis forms a positive loop in Th9 dysregulation of RA. Targeting this signalling axis presents a potential target approach for treating RA.
Keywords: Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Cytokines; T-Lymphocytes.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ on behalf of EULAR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

