CAR T-cell-mediated delivery of bispecific innate immune cell engagers for neuroblastoma
- PMID: 39164224
- PMCID: PMC11336212
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51337-2
CAR T-cell-mediated delivery of bispecific innate immune cell engagers for neuroblastoma
Abstract
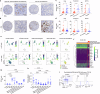
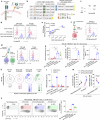
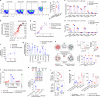
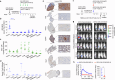
Novel chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell approaches are needed to improve therapeutic efficacy in solid tumors. High-risk neuroblastoma is an aggressive pediatric solid tumor that expresses cell-surface GPC2 and GD2 with a tumor microenvironment infiltrated by CD16a-expressing innate immune cells. Here we engineer T-cells to express a GPC2-directed CAR and simultaneously secrete a bispecific innate immune cell engager (BiCE) targeting both GD2 and CD16a. In vitro, GPC2.CAR-GD2.BiCE T-cells induce GPC2-dependent cytotoxicity and secrete GD2.BiCE that promotes GD2-dependent activation of antitumor innate immunity. In vivo, GPC2.CAR-GD2.BiCE T-cells locally deliver GD2.BiCE and increase intratumor retention of NK-cells. In mice bearing neuroblastoma patient-derived xenografts and reconstituted with human CD16a-expressing immune cells, GD2.BiCEs enhance GPC2.CAR antitumor efficacy. A CAR.BiCE strategy should be considered for tumor histologies where antigen escape limits CAR efficacy, especially for solid tumors like neuroblastoma that are infiltrated by innate immune cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.-P. and K.R.B. report having a pending patent directly related to this work entitled
Figures

References
-
- Hou, A. J., Chen, L. C. & Chen, Y. Y. Navigating CAR-T cells through the solid-tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.20, 531–550 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SU2C-AACR-DT-27-17/EIF | Stand Up To Cancer (SU2C)
- CA266914/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- K08 CA266914/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PST-07-16/Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (Cancer Research Fund of the Damon Runyon-Walter Winchell Foundation)
- K08 CA230223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

