Sex-specific cardiovascular risk factors in the UK Biobank
- PMID: 39165282
- PMCID: PMC11333928
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1339866
Sex-specific cardiovascular risk factors in the UK Biobank
Abstract
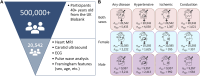
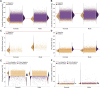
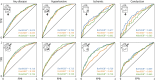
The lack of sex-specific cardiovascular disease criteria contributes to the underdiagnosis of women compared to that of men. For more than half a century, the Framingham Risk Score has been the gold standard to estimate an individual's risk of developing cardiovascular disease based on the age, sex, cholesterol levels, blood pressure, diabetes status, and the smoking status. Now, machine learning can offer a much more nuanced insight into predicting the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The UK Biobank is a large database that includes traditional risk factors and tests related to the cardiovascular system: magnetic resonance imaging, pulse wave analysis, electrocardiograms, and carotid ultrasounds. Here, we leverage 20,542 datasets from the UK Biobank to build more accurate cardiovascular risk models than the Framingham Risk Score and quantify the underdiagnosis of women compared to that of men. Strikingly, for a first-degree atrioventricular block and dilated cardiomyopathy, two conditions with non-sex-specific diagnostic criteria, our study shows that women are under-diagnosed 2× and 1.4× more than men. Similarly, our results demonstrate the need for sex-specific criteria in essential primary hypertension and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Our feature importance analysis reveals that out of the top 10 features across three sexes and four disease categories, traditional Framingham factors made up between 40% and 50%; electrocardiogram, 30%-33%; pulse wave analysis, 13%-23%; and magnetic resonance imaging and carotid ultrasound, 0%-10%. Improving the Framingham Risk Score by leveraging big data and machine learning allows us to incorporate a wider range of biomedical data and prediction features, enhance personalization and accuracy, and continuously integrate new data and knowledge, with the ultimate goal to improve accurate prediction, early detection, and early intervention in cardiovascular disease management. Our analysis pipeline and trained classifiers are freely available at https://github.com/LivingMatterLab/CardiovascularDiseaseClassification.
Keywords: UK Biobank; cardiovascular; heart disease; risk factors; sex differences.
Copyright © 2024 St. Pierre, Kaczmarski, Peirlinck and Kuhl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Abadi M., Agarwal A., Barham P., Brevdo E., Chen Z., Citro C., et al. (2016). TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv: 10.48550/arXiv.1603.04467 - DOI
-
- Aceña V., Martín de Diego I., Fernández R. R., Moguerza M. J. (2022). Minimally overfitted learners: a general framework for ensemble learning. Knowledge-Based Syst. 254, 109669. 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109669 - DOI
-
- Alber M., Buganza Tepole A., Cannon W., De S., Dura-Bernal S., Garikipati K., et al. (2019). Integrating machine learning and multiscale modeling: perspectives, challenges, and opportunities in the biological, biomedical, and behavioral sciences. npj Digit. Med. 2, 115. 10.1038/s41746-019-0193-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arik S. O., Pfister T. (2020). Tabnet: attentive interpretable tabular learning. arXiv : 10.48550/arXiv.1908.07442 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

