PTEN in kidney diseases: a potential therapeutic target in preventing AKI-to-CKD transition
- PMID: 39165377
- PMCID: PMC11333338
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1428995
PTEN in kidney diseases: a potential therapeutic target in preventing AKI-to-CKD transition
Abstract
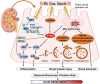
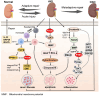
Renal fibrosis, a critical factor in the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD), is predominantly initiated by acute kidney injury (AKI) and subsequent maladaptive repair resulting from pharmacological or pathological stimuli. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), also known as phosphatase and tensin-associated phosphatase, plays a pivotal role in regulating the physiological behavior of renal tubular epithelial cells, glomeruli, and renal interstitial cells, thereby preserving the homeostasis of renal structure and function. It significantly impacts cell proliferation, apoptosis, fibrosis, and mitochondrial energy metabolism during AKI-to-CKD transition. Despite gradual elucidation of PTEN's involvement in various kidney injuries, its specific role in AKI and maladaptive repair after injury remains unclear. This review endeavors to delineate the multifaceted role of PTEN in renal pathology during AKI and CKD progression along with its underlying mechanisms, emphasizing its influence on oxidative stress, autophagy, non-coding RNA-mediated recruitment and activation of immune cells as well as renal fibrosis. Furthermore, we summarize prospective therapeutic targeting strategies for AKI and CKD-treatment related diseases through modulation of PTEN.
Keywords: AKI; AKI-to-CKD; CKD; PTEN; kidney.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Li, Peng, Li, Yang, Hu, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A short treatment with resveratrol after a renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury prevents maladaptive repair and long-term chronic kidney disease in rats.J Physiol. 2024 Apr;602(8):1835-1852. doi: 10.1113/JP285979. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38529522
-
PTEN alleviates maladaptive repair of renal tubular epithelial cells by restoring CHMP2A-mediated phagosome closure.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Nov 16;12(12):1087. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04372-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34789720 Free PMC article.
-
Akt1 is involved in renal fibrosis and tubular apoptosis in a murine model of acute kidney injury-to-chronic kidney disease transition.Exp Cell Res. 2023 Mar 15;424(2):113509. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113509. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Exp Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 36773738
-
From AKI to CKD: Maladaptive Repair and the Underlying Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10880. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810880. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway from Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease: Molecules Involved in Renal Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14019. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814019. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation is a promising therapy for kidney diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;12:1628722. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1628722. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40703302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

