Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: A Rare Congenital Disorder With Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 39165472
- PMCID: PMC11334947
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.65035
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: A Rare Congenital Disorder With Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a genetic multisystemic disorder with oculocutaneous albinism, granulomatous colitis, bleeding diathesis, and pulmonary fibrosis. Multiple subtypes of HPS exist, with certain types having higher predilection for pulmonary fibrosis. This case report focuses on the demonstration of pulmonary imaging findings seen in a patient. Several imaging features overlap with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis including traction bronchiectasis, pleural and peribronchovascular thickening, and reticulations. This case report highlights the differences seen in lung disease associated with HPS compared to other interstitial lung diseases, in addition to the multi-systemic features of HPS.
Keywords: ground-glass opacities; honeycombing; ild interstitial lung disease; pulmonary interstitial fibrosis; traction bronchiectasis.
Copyright © 2024, Sanampudi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
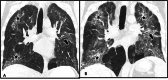

References
-
- Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. El-Chemaly S, Young LR. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2016.04.012. Clin Chest Med. 2016;37:505–511. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Genetic variants associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Merideth MA, Introne WJ, Wang JA, O'Brien KJ, Huizing M, Gochuico BR. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537104.2019.1663810. Platelets. 2020;31:544–547. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
