Reflex Xpert MTB/XDR Testing of Residual Rifampicin-Resistant Specimens: A Clinical Laboratory-Based Diagnostic Accuracy and Feasibility Study in South Africa
- PMID: 39165581
- PMCID: PMC11334068
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofae437
Reflex Xpert MTB/XDR Testing of Residual Rifampicin-Resistant Specimens: A Clinical Laboratory-Based Diagnostic Accuracy and Feasibility Study in South Africa
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization-approved Xpert MTB/XDR test detects Mycobacterium tuberculosis and resistance to isoniazid, fluoroquinolones, ethionamide, and injectable drugs directly in specimens. This pragmatic, laboratory-based study assessed the diagnostic accuracy and feasibility of a reflex testing approach, where Xpert MTB/XDR was performed on residual specimens previously processed for Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra.
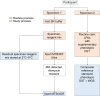
Methods: Routine respiratory specimens, processed for Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra, were stored in sample reagent buffer at 2°C-8°C. If rifampicin resistant, the residual specimen was assessed for adequate volume (≥2 mL) and tested with Xpert MTB/XDR, with storage time recorded. A second specimen was used for routine and reference standard testing (culture and sequencing).
Results: Specimens (99% sputum) from 763 participants submitted to 2 large routine laboratories were included. Xpert MTB/XDR yielded valid resistance detection results in 639 (84%), compared with 507 (66%) for routine testing (difference [95% CI], 18% [13%-22%]). The median turnaround time for results was 23 hours for Xpert MTB/XDR and 15 days for routine testing. While 748 specimens (98%) were ≥2 mL, only 102 (13%) were stored for ≤4 hours. By the reference standard, 284 of 394 (72%) were isoniazid resistant, and 57 of 380 (15%) were fluroquinolone resistant. The sensitivities of Xpert MTB/XDR were 94% (95% CI, 91%-97%) for isoniazid and 91% (81%-97%) for fluoroquinolone resistance detection. The specificities were 98% (94%-100%) and 100% (98%-100%), respectively.
Conclusions: Xpert MTB/XDR performed favorably compared with the reference, and the reflex testing approach increased results availability over routine testing, while dramatically decreasing turnaround time from weeks to hours. Laboratory workflow precluded testing within the manufacturer-recommended 4-hour storage time, but longer storage did not appear detrimental.
Keywords: Xpert MTB/XDR; diagnostic accuracy; drug resistance; feasibility; tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2023. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2023.
-
- World Health Organization . WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment—drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2022. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Use of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra on GeneXpert 10-colour instruments: WHO policy statement. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

