The clinical significance of endoplasmic reticulum stress related genes in non-small cell lung cancer and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism for CAV1
- PMID: 39165641
- PMCID: PMC11334084
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1414164
The clinical significance of endoplasmic reticulum stress related genes in non-small cell lung cancer and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism for CAV1
Abstract
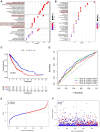
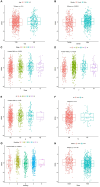
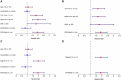
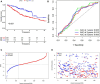
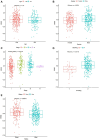
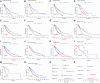
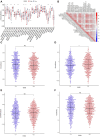
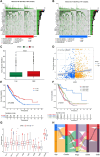
In recent years, protein homeostasis imbalance caused by endoplasmic reticulum stress has become a major hallmark of cancer. Studies have shown that endoplasmic reticulum stress is closely related to the occurrence, development, and drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer, however, the role of various endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in non-small cell lung cancer is still unclear. In this study, we established an endoplasmic reticulum stress scores based on the Cancer Genome Atlas for non-small cell lung cancer to reflect patient features and predict prognosis. Survival analysis showed significant differences in overall survival among non-small cell lung cancer patients with different endoplasmic reticulum stress scores. In addition, endoplasmic reticulum stress scores was significantly correlated with the clinical features of non-small cell lung cancer patients, and can be served as an independent prognostic indicator. A nomogram based on endoplasmic reticulum stress scores indicated a certain clinical net benefit, while ssGSEA analysis demonstrated that there was a certain immunosuppressive microenvironment in high endoplasmic reticulum stress scores. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis showed that scores was associated with cancer pathways and metabolism. Finally, weighted gene co-expression network analysis displayed that CAV1 was closely related to the occurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Therefore, in order to further analyze the role of this gene, Chinese non-smoking females were selected as the research subjects to investigate the relationship between CAV1 rs3779514 and susceptibility and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. The results showed that the mutation of rs3779514 significantly reduced the risk of non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese non-smoking females, but no prognostic effect was found. In summary, we proposed an endoplasmic reticulum stress scores, which was an independent prognostic factor and indicated immune characteristics in the microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer. We also validated the relationship between single nucleotide polymorphism locus of core genes and susceptibility to non-small cell lung cancer.
Keywords: CAV1; bioinformatics; endoplasmic reticulum stress; non-small cell lung cancer; single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Chen and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma based on endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 18;12(1):19857. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23852-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36400857 Free PMC article.
-
A risk score model based on endoplasmic reticulum stress related genes for predicting prognostic value of osteosarcoma.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Jun 23;24(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06629-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37353812 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-related signature to evaluate immune features and predict prognosis in glioma.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Apr;25(8):3870-3884. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16321. Epub 2021 Feb 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33611848 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and clinical features of endoplasmic reticulum stress factor in digestive system pan-cancer studies.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 9;12:1072576. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1072576. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36698399 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omic analysis and experiment reveals the role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jan 2;17(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01785-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38167084 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression Profiling Identifies CAV1, CD44, and TFRC as Potential Diagnostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets for Multiple Myeloma.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01743-0. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40246772
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

