Comparison Study of the Bio-Plex and Meso Scale Multiplexed SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assays Reveals Evidence of Diminished Host Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 after Monoclonal Antibody Treatment
- PMID: 39165724
- PMCID: PMC11335343
- DOI: 10.20411/pai.v9i2.715
Comparison Study of the Bio-Plex and Meso Scale Multiplexed SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assays Reveals Evidence of Diminished Host Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 after Monoclonal Antibody Treatment
Abstract
Background: Assessing the breadth and duration of antigen-specific binding antibodies provides valuable information for evaluating interventions to treat or prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Multiplex immunoassays are a convenient method for rapid measurement of antibody responses but can sometimes provide discordant results, and antibody positive percent agreement for COVID-19 diagnosis can vary depending on assay type, disease severity, and population sampled. Therefore, we compared two assays marked for research applications, MSD and Bio-Plex Pro, to evaluate qualitative interpretation of serostatus and quantitative detection of antibodies of varying isotypes (IgG, IgM, and IgA) against receptor binding domain (RBD) and nucleocapsid (N) antigens.
Methods: Specimens from ACTIV-2/A5401, a placebo-controlled clinical trial of the SARSCoV-2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) bamlanivimab to prevent COVID-19 disease progression, were used to evaluate the concordance of the Bio-Rad Bio-Plex Pro Human SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assay and the Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) V-PLEX COVID-19 Panel 1 serology assay in detecting and quantifying IgG, IgA, and IgM binding anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses against the RBD and N antigens. Data were disaggregated by study arm, bamlanivimab dose, days post-enrollment, and presence of emerging resistance.
Results: We observed 90.5% (412 of 455 tests) concordance for anti-RBD IgG and 87% (396 of 455) concordance for anti-N IgG in classifying samples as negative or positive based on assay-defined cutoffs. Antibody levels converted to the WHO standard BAU/mL were significantly correlated for all isotypes (IgG, IgM, and IgA) and SARS-CoV-2 antigen targets (RBD and N) tested that were common between the two assays (Spearman r 0.65 to 0.92, P < 0.0001). Both assays uncovered evidence of diminished host-derived IgG immune responses in participants treated with bamlanivimab compared to placebo. Assessment of immune responses in the four individuals treated with the 700 mg of bamlanivimab with emerging mAb resistance demonstrated a stronger anti-N IgG response (MSD) at day 28 (median 2.18 log BAU/mL) compared to participants treated with bamlanivimab who did not develop resistance (median 1.55 log BAU/mL).
Conclusions: These data demonstrate the utility in using multiplex immunoassays for characterizing the immune responses with and without treatment in a study population and provide evidence that monoclonal antibody treatment in acute COVID-19 may have a modest negative impact on development of host IgG responses.
Keywords: Bio-Plex; COVID; COVID-19; Meso Scale Discovery; SARS-CoV-2; bamlanivimab; monoclonal antibodies.
Copyright © 2024 Pathogens and Immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
U.M.P. has consulted for Merck unrelated to the current work. J.W.M. is a consultant to Gilead Sciences, Inc. and has received grant funding from Gilead Sciences, Inc. to the University of Pittsburgh (unrelated to the current work); receives compensation from Galapagos NV (unrelated to the current work); and holds share options in Galapagos NV, Infectious Disease Connect, Inc., and MingMed Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (unrelated to the current work). A.L.L. has consulted for Gilead and Abbott. J.S.C. has served on a Merck Advisory Board. J.J.E. is a consultant to Merck and Gilead and has received research funding to his institution from Gilead; he is also on a Data Safety Monitoring Committee for Invivyd. K.W.C. has received research funding to the institution from Merck Sharp & Dohme and has consulted for Pardes Biosciences. D.M.S. has consulted for Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Linear Therapies, Model Medicines, Fluxergy, and Vx Biosciences. J.Z.L. has consulted for Abbvie.
Figures
 ); 700 mg placebo (light blue circles
); 700 mg placebo (light blue circles  ); 7,000 mg bamlanivimab (dark orange diamonds
); 7,000 mg bamlanivimab (dark orange diamonds  ); 7,000 mg placebo (dark blue diamonds
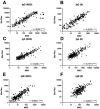
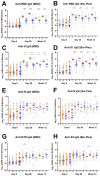
); 7,000 mg placebo (dark blue diamonds  ). Each arm is plotted from samples collected at baseline (day 0, within 10 days of symptom onset), day 28, and week 12 post-enrollment. For Bio-Plex, seronegative samples whose BAU/mL was under the limit of quantitation could not be plotted thus were omitted from the graph. The median log BAU/mL for each data set is indicated by a solid line. The number of samples plotted is noted under the x-axis. The dashed horizontal line from the y-axis denotes the log BAU/mL value under which the sample is classified as IgG negative; these values are set at (A) 1.17 (anti-RBD IgG MSD); (B) 0.83 (anti-RBD IgG Bio-Plex); (C) 1.25 (anti-S IgG MSD); (D) 0.74 (anti-S1 IgG Bio-Plex); (E) 1.07 (anti-N IgG MSD); (F) 0.56 (anti-N IgG Bio-Plex); (G) no qualitative cutoff is available for anti-NTD IgG MSD; and (H) 0.72 (anti-S2 IgG Bio-Plex). Mann-Whitney test was used to compare unpaired ranked log BAU/mL for each arm (700 mg or 7,000 mg bamlanivimab) against its corresponding placebo arm for each time point of collection. Comparisons are denoted as follows: not significant (ns); P ≤ 0.05 (*); P ≤ 0.01 (**); P ≤ 0.001 (***) and P ≤ 0.0001 (****).
). Each arm is plotted from samples collected at baseline (day 0, within 10 days of symptom onset), day 28, and week 12 post-enrollment. For Bio-Plex, seronegative samples whose BAU/mL was under the limit of quantitation could not be plotted thus were omitted from the graph. The median log BAU/mL for each data set is indicated by a solid line. The number of samples plotted is noted under the x-axis. The dashed horizontal line from the y-axis denotes the log BAU/mL value under which the sample is classified as IgG negative; these values are set at (A) 1.17 (anti-RBD IgG MSD); (B) 0.83 (anti-RBD IgG Bio-Plex); (C) 1.25 (anti-S IgG MSD); (D) 0.74 (anti-S1 IgG Bio-Plex); (E) 1.07 (anti-N IgG MSD); (F) 0.56 (anti-N IgG Bio-Plex); (G) no qualitative cutoff is available for anti-NTD IgG MSD; and (H) 0.72 (anti-S2 IgG Bio-Plex). Mann-Whitney test was used to compare unpaired ranked log BAU/mL for each arm (700 mg or 7,000 mg bamlanivimab) against its corresponding placebo arm for each time point of collection. Comparisons are denoted as follows: not significant (ns); P ≤ 0.05 (*); P ≤ 0.01 (**); P ≤ 0.001 (***) and P ≤ 0.0001 (****).
References
-
- Marra AR, Kobayashi T, Suzuki H, Alsuhaibani M, Tofaneto BM, Bariani LM, Auler MA, Salinas JL, Edmond MB, Doll M, Kutner JM, Pinho JRR, Rizzo LV, Miraglia JL, Schweizer ML. Short-term effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in immunocompromised patients: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2022;84(3):297–310. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.12.035. PubMed PMID: 34982962; PMCID: PMC8720049. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Zhang L, Xie YH, Wu J. Advancements in detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection for confronting COVID-19 pandemics. Lab Invest. 2022;102(1):4–13. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00663-w. PubMed PMID: 34497366; PMCID: PMC8424153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moser C, Li JZ, Eron JJ, Aga E, Daar ES, Wohl DA, Coombs RW, Javan AC, Bender Ignacio RA, Jagannathan P, Ritz J, Sieg SF, Parikh UM, Hughes MD, Currier JS, Smith DM, Chew KW, Team A-AS. Predictors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA From Nasopharyngeal Swabs and Concordance With Other Compartments in Nonhospitalized Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022;9(11):ofac618. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac618. PubMed PMID: 36467293; PMCID: PMC9709705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fox T, Geppert J, Dinnes J, Scandrett K, Bigio J, Sulis G, Hettiarachchi D, Mathangasinghe Y, Weeratunga P, Wickramasinghe D, Bergman H, Buckley BS, Probyn K, Sguassero Y, Davenport C, Cunningham J, Dittrich S, Emperador D, Hooft L, Leeflang MM, McInnes MD, Spijker R, Struyf T, Van den Bruel A, Verbakel JY, Takwoingi Y, Taylor-Phillips S, Deeks JJ, Cochrane C-DTAG. Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. PubMed PMID: 36394900; PMCID: PMC9671206. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kenny G, Negi R, O'Reilly S, Garcia-Leon A, Alalwan D, Gaillard CM, Saini G, Inzitari R, Feeney ER, Yousif O, Cotter AG, de Barra E, Sadlier C, Crispie F, Doran P, Gautier V, Mallon PWG, s All Ireland Infectious Diseases cohort. Performance and validation of an adaptable multiplex assay for detection of serologic response to SARSCoV-2 infection or vaccination. J Immunol Methods. 2022;510:113345. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113345. PubMed PMID: 36055441; PMCID: PMC9425705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
