Diagnosis of a Rare Rickettsia felis Infection Complicated with Unusual Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade Using an mNGS Test
- PMID: 39165786
- PMCID: PMC11335410
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/8877876
Diagnosis of a Rare Rickettsia felis Infection Complicated with Unusual Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade Using an mNGS Test
Abstract
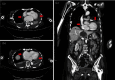
The occurrence of sporadic rickettsial infections has been consistently undervalued and overlooked, primarily owing to a limited emphasis on routine examinations for rickettsioses in clinical practice. At present, the immunofluorescence assay is the prevailing diagnostic method for suspected rickettsioses that enables the detection of specific antibodies against rickettsia in human serum. Herein, we present an exceptional instance of rickettsial infection that was characterized by a rare manifestation of extensive pericardial effusion leading to dyspnea and cardiac tamponade. A diagnosis of chronic fibrosing pericarditis was established based on pericardium tissue obtained through pericardiotomy, and a conclusive metagenomic next-generation sequencing test confirmed the presence of Rickettsia felis infection. The cat flea, scientifically known as Ctenocephalides felis, is the predominant carrier of R. felis. An escalating incidence of human R. felis infections has raised concerns, particularly in light of the burgeoning population of domesticated animals in many contemporary societies.
Copyright © 2024 Tien-Lung Po et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Rickettsia Species in Fleas Collected from Cats in Regions Endemic and Nonendemic for Flea-Borne Rickettsioses in California.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016 Mar;16(3):151-6. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2015.1869. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016. PMID: 26824189
-
Rickettsial Infections among Ctenocephalides felis and Host Animals during a Flea-Borne Rickettsioses Outbreak in Orange County, California.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 18;11(8):e0160604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160604. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27537367 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsial Infections among Cats and Cat Fleas in Riverside County, California.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018 Aug;99(2):291-296. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0706. Epub 2018 May 31. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018. PMID: 29869607 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsia felis is an emerging human pathogen associated with cat fleas: A review of findings in Taiwan.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2023 Feb;56(1):10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2022.12.006. Epub 2022 Dec 17. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2023. PMID: 36585292 Review.
-
Manifestations and Management of Flea-Borne Rickettsioses.Res Rep Trop Med. 2021 Feb 5;12:1-14. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S274724. eCollection 2021. Res Rep Trop Med. 2021. PMID: 33574726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biggs H. M., Behravesh C. B., Bradley K. K., et al. Diagnosis and management of tickborne rickettsial diseases: Rocky mountain spotted fever and other spotted fever group rickettsioses, ehrlichioses, and anaplasmosis - United States. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports . 2016;65(2):1–44. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.rr6502a1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

