S-Alkylated quinazolin-4(3 H)-ones as dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 kinases inhibitors: design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation and docking study
- PMID: 39165788
- PMCID: PMC11333997
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra04828h
S-Alkylated quinazolin-4(3 H)-ones as dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 kinases inhibitors: design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation and docking study
Abstract
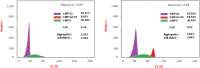
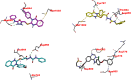
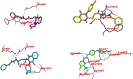
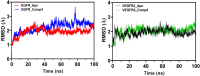
Dual targeting by a single molecule has emerged as a promising strategy for fighting cancer. In this study, a new set of 2-thioquinazolin-4(3H)-ones as potential anti-cancer surrogates endowed with dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 kinases inhibitory activities were synthesized. The anti-tumor potency of the newly synthesized candidates 4-27 was evaluated against a panel of four cancer cell lines. The prepared candidates 4-27 showed comparable activity to that of the standard drug sorafenib. For instance, compound 4 (IC50 = 1.50-5.86 μM) and compound 20 (IC50 = 4.42-6.39 μM) displayed superior potencies against all cell lines compared to sorafenib (IC50 = 5.47-7.26 μM). Dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibitory activities of the most active analogues (4, 11, and 20) were investigated. Compound 4 showed comparable EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibitory activity to the used control drugs. Flow cytometric analysis indicates that the most potent analogue 4 stopped the cell cycle at the G1 phase and induced 46.53% total apoptosis in HCT-116 cells that was much more powerful than the untreated cells with 2.15% apoptosis. Molecular docking and dynamic simulations of 4, 11, and 20 with EGFR and VEGFR-2 were performed to examine the binding mode and interaction within the enzyme binding pockets.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design, molecular docking, in vitro, and in vivo studies of new quinazolin-4(3H)-ones as VEGFR-2 inhibitors with potential activity against hepatocellular carcinoma.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Feb;107:104532. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104532. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33334586
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
-
Discovery of new quinazolin-4(3H)-ones as VEGFR-2 inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and anti-proliferative evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Dec;105:104380. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104380. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33128967
-
EGFR/VEGFR-2 dual inhibitor and apoptotic inducer: Design, synthesis, anticancer activity and docking study of new 2-thioxoimidazolidin-4one derivatives.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119531. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119531. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33887348
-
Targeting the interplay between MMP-2, CA II and VEGFR-2 via new sulfonamide-tethered isomeric triazole hybrids; Microwave-assisted synthesis, computational studies and evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Jul;124:105816. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105816. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35489270 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, and in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation of triazolopyrimidine hybrids as multitarget directed anticancer agents.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 7;14(48):35239-35254. doi: 10.1039/d4ra06704e. eCollection 2024 Nov 4. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39512645 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the investigation of the quinazoline nucleus and derivatives with potential anticancer activities.Future Med Chem. 2025 May;17(10):1193-1211. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2507558. Epub 2025 May 30. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40444391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, antiproliferative potency, and in silico studies of novel 5-methylfuran-3-yl)thio)-3-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one based derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 31;15(1):27992. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12140-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40745188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marklew R. E. Jackson A. A. Wiseman M. J. Wootton S. A. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;130:3–10.
-
- Hamdi A. Said E. A Farahat A. AA El-Bialy S. AM Massoud M. Lett. Drug Des. Discovery. 2016;13:912–920.
-
- Sung H. Ferlay J. Siegel R. L. Laversanne M. Soerjomataram I. Jemal A. Bray F. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Christiea E. L. Bowtell D. D. L. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:viii13–viii15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

