Intermittent theta-burst stimulation in aphasia caused by right side cerebral lesions after stroke: A case report with 2-year follow-up
- PMID: 39166089
- PMCID: PMC11333899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35206
Intermittent theta-burst stimulation in aphasia caused by right side cerebral lesions after stroke: A case report with 2-year follow-up
Abstract
Background and objectives: This case report investigates the application of intermittent Theta-Burst Stimulation (iTBS) in aphasia rehabilitation following a right hemisphere stroke.
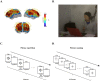
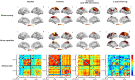
Case presentation: A 52-year-old Chinese male with Broca's aphasia post-stroke was treated with iTBS. His progress was evaluated using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) and behavioral assessments. Significant language function improvement was noted, with fNIRS showing increased activation in right hemisphere language-related cortical areas and altered functional connectivity patterns.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that iTBS is effective in facilitating language recovery in right hemisphere stroke-induced aphasia, highlighting the importance of personalized neurorehabilitation strategies. Despite focusing on a single case, the study contributes to understanding neural plasticity mechanisms in right hemisphere stroke-induced aphasia.
Keywords: Aphasia; Functional near-infrared spectroscopy; Intermittent theta-burst stimulation; Neural plasticity; Stroke.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of the manuscript entitled.
Figures

References
-
- Flowers H.L., Skoretz S.A., Silver F.L., et al. Poststroke aphasia frequency, recovery, and outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016;97(12):2188–2201.e2188. - PubMed
-
- Mariën P., Paghera B., De Deyn P.P., Vignolo L.A. Adult crossed aphasia in dextrals revisited. Cortex; a journal devoted to the study of the nervous system and behavior. 2004;40(1):41–74. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

