Developing poly(ethylene glycol)- b-poly(β-hydroxybutyrate)-based self-assembling prodrug for the management of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 39166178
- PMCID: PMC11334744
- DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2024.2382084
Developing poly(ethylene glycol)- b-poly(β-hydroxybutyrate)-based self-assembling prodrug for the management of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
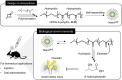
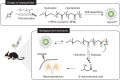
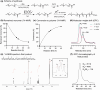
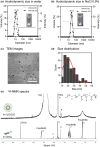
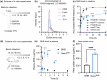
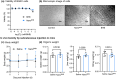
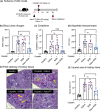
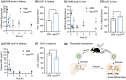
Although β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), one of the endogenous body ketones, possesses high bioactivities, it is rapidly consumed, metabolized, and eliminated from the body. In this study, we designed new self-assembling nanoparticles that sustainably released BHB to improve bioavailability and evaluated their efficacy in in vivo experiments using rodent animal models. Since poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) [poly(BHB)] is regarded as a polymeric prodrug that is hydrolyzed by endogenous enzymes and releases BHB in a sustained manner, our idea was to engineer hydrophobic poly(BHB) in one of the segments in the amphiphilic block copolymer, of which self-assembles in water to form nanoparticles of tens of nanometers in size (abbreviated as NanoBHB). Here, methoxy-poly(ethylene glycol) was employed as the hydrophilic segment of the block copolymer to stabilize the nanoparticles in aqueous environments, thus enabling NanoBHBs to be administrable both orally and through injection. Experimental results showed that NanoBHB has low toxicity and releases free BHB for an extended period in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, NanoBHB exhibits superior nephroprotective effects in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury mouse models compared to low-molecular-weight (LMW) sodium BHB, suggesting the potential of NanoBHB as a sustainable release formulation to supply BHB for medicinal applications.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; ketone bodies; nanoparticles; poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(β-hydroxybutyrate); β-hydroxybutyrate.
Plain language summary
We engineered self-assembling poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(D,L-β-hydroxybutyrate) nanoparticles as a prodrug for continuous release of β-hydroxybutyrate, inducing bioactivity as a ketone body and providing nephroprotective properties against acute kidney injuries.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by National Institute for Materials Science in partnership with Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Xiang Y, Wang Q-Q, Lan X-Q, et al. Function and treatment strategies of β-hydroxybutyrate in aging. Smart Mater Med. 2023;4:160–172. doi: 10.1016/j.smaim.2022.09.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
