Cleansing efficacy of the electric toothbrush Oral-B® iO™ compared to conventional oscillating-rotating technology: a randomized-controlled study
- PMID: 39167335
- PMCID: PMC11339098
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-024-05882-1
Cleansing efficacy of the electric toothbrush Oral-B® iO™ compared to conventional oscillating-rotating technology: a randomized-controlled study
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to compare the cleansing efficacy of the Oral-B® iO™ electric toothbrush incorporating oscillating-rotating technology with microvibrations - with a traditional oscillating-rotating toothbrush.
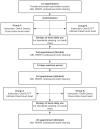
Materials and methods: Thirty adult participants were randomly assigned to use the iO™ electric toothbrush with the brush head iO™ Ultimate Clean or the traditional oscillating-rotating toothbrush Oral-B® Genius® with the Cross-Action brush head. Oral hygiene indices (Rustogi Modified Navy Plaque Index and Gingival Bleeding Index) were assessed before and after 28 days of home use of the assigned product. Participants were instructed to refrain from interdental hygiene during the study period. After a 2-week washout period, the clinical investigation was repeated in a crossover design.
Results: All 30 participants completed the study with no dropouts. After 28 days of use, the iO™ showed statistically significantly lower plaque levels than the conventional oscillating-rotating toothbrush (25.09% vs. 30.60%, p = 0.029). This difference was particularly noticeable in marginal and approximal areas. There were no significant distinctions in gingival bleeding indices.
Conclusions: The Oral-B® iO™ electric toothbrush displayed enhanced plaque removal efficiency compared to a conventional oscillating-rotating technology.
Clinical relevance: This study highlights the potential benefits of advanced toothbrush technologies for plaque reduction and encourages further research.
Keywords: Biofilm; Oral hygiene; Plaque reduction; Powered toothbrush.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Davidovich E, Shafir S, Shay B, Zini A (2020) Plaque removal by a Powered Toothbrush Versus a Manual Toothbrush in children: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Pediatr Dent 42:280–287 - PubMed
-
- P FGU, K. C-Z MW, R G, P. W (2020) Bristle motion, forces and related vertical translation for a novel electric toothbrush design. J Mech Eng 66:7
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

