Integrative Multiomics in the Lung Reveals a Protective Role of Asporin in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 39167456
- PMCID: PMC11473243
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069864
Integrative Multiomics in the Lung Reveals a Protective Role of Asporin in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Integrative Multiomics in the Lung Reveals a Protective Role of Asporin in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Circulation. 2025 Apr 8;151(14):e921. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001331. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 40193543 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Integrative multiomics can elucidate pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) pathobiology, but procuring human PAH lung samples is rare.
Methods: We leveraged transcriptomic profiling and deep phenotyping of the largest multicenter PAH lung biobank to date (96 disease and 52 control) by integration with clinicopathologic data, genome-wide association studies, Bayesian regulatory networks, single-cell transcriptomics, and pharmacotranscriptomics.
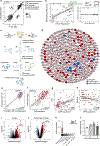
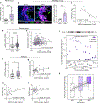
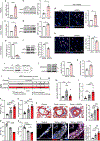
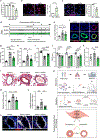
Results: We identified 2 potentially protective gene network modules associated with vascular cells, and we validated ASPN, coding for asporin, as a key hub gene that is upregulated as a compensatory response to counteract PAH. We found that asporin is upregulated in lungs and plasma of multiple independent PAH cohorts and correlates with reduced PAH severity. We show that asporin inhibits proliferation and transforming growth factor-β/phosphorylated SMAD2/3 signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from PAH lungs. We demonstrate in Sugen-hypoxia rats that ASPN knockdown exacerbated PAH and recombinant asporin attenuated PAH.
Conclusions: Our integrative systems biology approach to dissect the PAH lung transcriptome uncovered asporin as a novel protective target with therapeutic potential in PAH.
Keywords: gene expression profiling; multiomics; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs Hong, Medzikovic, and Eghbali are coinventors of US provisional patent application 63/544,027, “Asporin in Pulmonary Hypertension.”
Figures


References
-
- Porcu E, Sadler MC, Lepik K, Auwerx C, Wood AR, Weihs A, Sleiman MSB, Ribeiro DM, Bandinelli S, Tanaka T, Nauck M, Völker U, Delaneau O, Metspalu A, Teumer A, Frayling T, Santoni FA, Reymond A, Kutalik Z. Differentially expressed genes reflect disease-induced rather than disease-causing changes in the transcriptome. Nat Commun. Nature Publishing Group; 2021. Sep 24;12(1):5647. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shu L, Zhao Y, Kurt Z, Byars SG, Tukiainen T, Kettunen J, Orozco LD, Pellegrini M, Lusis AJ, Ripatti S, Zhang B, Inouye M, Mäkinen VP, Yang X. Mergeomics: multidimensional data integration to identify pathogenic perturbations to biological systems. BMC Genomics. 2016. Nov 4;17(1):874. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

