Global expansion of human-wildlife overlap in the 21st century
- PMID: 39167651
- PMCID: PMC11338222
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp7706
Global expansion of human-wildlife overlap in the 21st century
Abstract
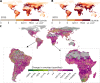
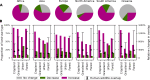
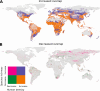
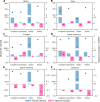
Understanding the extent to which people and wildlife overlap in space and time is critical for the conservation of biodiversity and ecological services. Yet, how global change will reshape the future of human-wildlife overlap has not been assessed. We show that the potential spatial overlap of global human populations and 22,374 terrestrial vertebrate species will increase across ~56.6% and decrease across only ~11.8% of the Earth's terrestrial surface by 2070. Increases are driven primarily by intensification of human population densities, not change in wildlife distributions caused by climate change. The strong spatial heterogeneity of future human-wildlife overlap found in our study makes it clear that local context is imperative to consider, and more targeted area-based land-use planning should be integrated into systematic conservation planning.
Figures
References
-
- Barnosky A. D., Hadly E. A., Bascompte J., Berlow E. L., Brown J. H., Fortelius M., Getz W. M., Harte J., Hastings A., Marquet P. A., Martinez N. D., Mooers A., Roopnarine P., Vermeij G., Williams J. W., Gillespie R., Kitzes J., Marshall C., Matzke N., Mindell D. P., Revilla E., Smith A. B., Approaching a state shift in Earth’s biosphere. Nature 486, 52–58 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Carter N. H., Linnell J. D. C., Co-adaptation is key to coexisting with large carnivores. Trends Ecol. Evol. 31, 575–578 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Ceauşu S., Graves R. A., Killion A. K., Svenning J. C., Carter N. H., Governing trade-offs in ecosystem services and disservices to achieve human–wildlife coexistence. Conserv. Biol. 33, 543–553 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

