Camu-camu decreases hepatic steatosis and liver injury markers in overweight, hypertriglyceridemic individuals: A randomized crossover trial
- PMID: 39168095
- PMCID: PMC11384942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101682
Camu-camu decreases hepatic steatosis and liver injury markers in overweight, hypertriglyceridemic individuals: A randomized crossover trial
Abstract
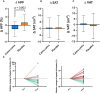
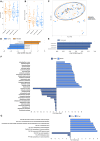
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 25% of the adult population with no effective drug treatments available. Previous animal studies reported that a polyphenol-rich extract from the Amazonian berry camu-camu (CC) prevented hepatic steatosis in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. This study aims to determine the impact of CC on hepatic steatosis (primary outcome) and evaluate changes in metabolic and gut microbiota profiles (exploratory outcomes). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial is conducted on 30 adults with overweight and hypertriglyceridemia, who consume 1.5 g of CC capsules or placebo daily for 12 weeks. CC treatment decreases liver fat by 7.43%, while it increases by 8.42% during the placebo intervention, showing a significant difference of 15.85%. CC decreases plasma aspartate and alanine aminotransferases levels and promotes changes in gut microbiota composition. These findings support that polyphenol-rich prebiotic may reduce liver fat in adults with overweight, reducing the risk of developing NAFLD.
Keywords: aminotransferases; camu-camu; gut microbiota; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; polyphenols.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A. Morissette, L.D., and T.G. received studentship from Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé (FRQS). A.-L.A. is supported by the Fondation du Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Québec. A. Marette holds a Pfizer/CIHR Partnered Research Chair on the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases. Y.D. holds an NSERC-Diana Food Industrial Partnership Chair on prebiotic effects of polyphenols. M.-C.V. is the recipient of a Canada Research Chair in Genomics Applied to Nutrition and Metabolic Health. A.-M.C. and C.G. received a career award from the FRQS.
Figures



References
-
- Koutoukidis D.A., Astbury N.M., Tudor K.E., Morris E., Henry J.A., Noreik M., Jebb S.A., Aveyard P. Association of Weight Loss Interventions With Changes in Biomarkers of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019;179:1262–1271. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.2248. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

