The JAK-STAT pathway: from structural biology to cytokine engineering
- PMID: 39169031
- PMCID: PMC11339341
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-01934-w
The JAK-STAT pathway: from structural biology to cytokine engineering
Erratum in
-
Correction: The JAK-STAT pathway: from structural biology to cytokine engineering.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 17;9(1):290. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01975-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39419998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway serves as a paradigm for signal transduction from the extracellular environment to the nucleus. It plays a pivotal role in physiological functions, such as hematopoiesis, immune balance, tissue homeostasis, and surveillance against tumors. Dysregulation of this pathway may lead to various disease conditions such as immune deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, hematologic disorders, and cancer. Due to its critical role in maintaining human health and involvement in disease, extensive studies have been conducted on this pathway, ranging from basic research to medical applications. Advances in the structural biology of this pathway have enabled us to gain insights into how the signaling cascade operates at the molecular level, laying the groundwork for therapeutic development targeting this pathway. Various strategies have been developed to restore its normal function, with promising therapeutic potential. Enhanced comprehension of these molecular mechanisms, combined with advances in protein engineering methodologies, has allowed us to engineer cytokines with tailored properties for targeted therapeutic applications, thereby enhancing their efficiency and safety. In this review, we outline the structural basis that governs key nodes in this pathway, offering a comprehensive overview of the signal transduction process. Furthermore, we explore recent advances in cytokine engineering for therapeutic development in this pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

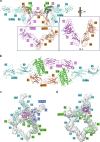

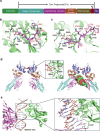
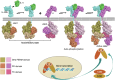
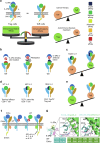



References
-
- Isaacs, A., Lindenmann, J. & Andrewes, C. H. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci.147, 258–267 (1957). - PubMed
-
- Isaacs, A., Lindenmann, J., Valentine, R. C. & Andrewes, C. H. Virus interference. II. Some properties of interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci.147, 268–273 (1957). - PubMed
-
- Levy, D. E. et al. Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev2, 383–393 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Levy, D. E., Kessler, D. S., Pine, R. & Darnell, J. E. Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev3, 1362–1371 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

