GENOMES UNCOUPLED PROTEIN1 binds to plastid RNAs and promotes their maturation
- PMID: 39169625
- PMCID: PMC11671767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101069
GENOMES UNCOUPLED PROTEIN1 binds to plastid RNAs and promotes their maturation
Abstract
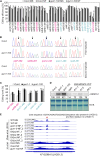
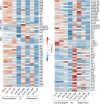
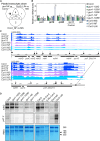
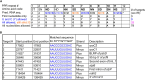
Plastid biogenesis and the coordination of plastid and nuclear genome expression through anterograde and retrograde signaling are essential for plant development. GENOMES UNCOUPLED1 (GUN1) plays a central role in retrograde signaling during early plant development. The putative function of GUN1 has been extensively studied, but its molecular function remains controversial. Here, we evaluate published transcriptome data and generate our own data from gun1 mutants grown under signaling-relevant conditions to show that editing and splicing are not relevant for GUN1-dependent retrograde signaling. Our study of the plastid (post)transcriptome of gun1 seedlings with white and pale cotyledons demonstrates that GUN1 deficiency significantly alters the entire plastid transcriptome. By combining this result with a pentatricopeptide repeat code-based prediction and experimental validation by RNA immunoprecipitation experiments, we identified several putative targets of GUN1, including tRNAs and RNAs derived from ycf1.2, rpoC1, and rpoC2 and the ndhH-ndhA-ndhI-ndhG-ndhE-psaC-ndhD gene cluster. The absence of plastid rRNAs and the significant reduction of almost all plastid transcripts in white gun1 mutants account for the cotyledon phenotype. Our study provides evidence for RNA binding and maturation as the long-sought molecular function of GUN1 and resolves long-standing controversies. We anticipate that our findings will serve as a basis for subsequent studies on mechanisms of plastid gene expression and will help to elucidate the function of GUN1 in retrograde signaling.
Keywords: GUN1; MORF2; RIP-seq; RNA binding protein; plastid (post)transcriptome; retrograde signaling.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GUN1 interacts with MORF2 to regulate plastid RNA editing during retrograde signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 14;116(20):10162-10167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1820426116. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30988197 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the transcription factor ANAC017 results in a genomes uncoupled phenotype under lincomycin.Plant J. 2024 Oct;120(1):91-108. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16973. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 39145415
-
Functional conservation of GENOMES UNCOUPLED1 in plastid-to-nucleus retrograde signaling in tomato.Plant Sci. 2024 Jun;343:112053. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112053. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38417718
-
The plastid transcription machinery and its coordination with the expression of nuclear genome: Plastid-Encoded Polymerase, Nuclear-Encoded Polymerase and the Genomes Uncoupled 1-mediated retrograde communication.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;375(1801):20190399. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0399. Epub 2020 May 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32362266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GUN1 and Plastid RNA Metabolism: Learning from Genetics.Cells. 2020 Oct 16;9(10):2307. doi: 10.3390/cells9102307. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33081381 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Holistic Investigation of Arabidopsis Proteomes Altered in Chloroplast Biogenesis and Retrograde Signalling Identifies PsbO as a Key Regulator of Chloroplast Quality Control.Plant Cell Environ. 2025 Aug;48(8):6373-6396. doi: 10.1111/pce.15611. Epub 2025 May 14. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. PMID: 40366233 Free PMC article.
-
Plastids in a Pinch: Coordinating Stress and Developmental Responses Through Retrograde Signalling.Plant Cell Environ. 2025 Sep;48(9):6897-6911. doi: 10.1111/pce.15664. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. PMID: 40474490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afgan E., Baker D., van den Beek M., Blankenberg D., Bouvier D., Čech M., Chilton J., Clements D., Coraor N., Eberhard C., et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W3–W10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw343. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

