Identifying factors related to mortality of hospitalized COVID-19 patients using machine learning methods
- PMID: 39170355
- PMCID: PMC11337730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35561
Identifying factors related to mortality of hospitalized COVID-19 patients using machine learning methods
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact globally, presenting significant social and economic challenges. This study aims to explore the factors affecting mortality among hospitalized COVID-19 patients and construct a machine learning-based model to predict the risk of mortality.
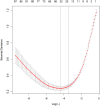
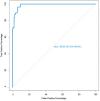
Methods: The study examined COVID-19 patients admitted to Imam Reza Hospital in Tabriz, Iran, between March 2020 and November 2021. The Elastic Net method was employed to identify and rank features associated with mortality risk. Subsequently, an artificial neural network (ANN) model was developed based on these features to predict mortality risk. The performance of the model was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results: The study included 706 patients with 96 features, out of them 26 features were identified as crucial predictors of mortality. The ANN model, utilizing 20 of these features, achieved an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 98.8 %, effectively stratifying patients by mortality risk.
Conclusion: The developed model offers accurate and precipitous mortality risk predictions for COVID-19 patients, enhancing the responsiveness of healthcare systems to high-risk individuals.
Keywords: Artificial neural network; COVID-19; Elastic net; Feature selection; LASSO; Machine learning; Mortality.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard DlupC, https://covid19.who.int/. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

