The relationship between anxiety and depression in adolescent depression patients: The mediating effect of hope level and coping modes
- PMID: 39170457
- PMCID: PMC11336736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35466
The relationship between anxiety and depression in adolescent depression patients: The mediating effect of hope level and coping modes
Abstract
Background: Adolescents diagnosed with depression are particularly susceptible to anxiety and depressive symptoms, this vulnerability often diminishes their future expectations and overall outlook on life. The objective of this research was to scrutinize the associated risk factors of adolescent depression and delineated the interplay between anxiety and depressive symptoms. Concurrently, it sought to ascertain the latent mediating effects of hope levels and coping strategies within this framework.
Methods: A mixed-methods research approach was employed. For the qualitative component, 18 adolescents with depression were interviewed following a semi-structured interview guide, with sessions audio-recorded. The data were subsequently transcribed and subjected to thematic content analysis. In the quantitative phase, a cross-sectional online survey was administered to 210 adolescents diagnosed with depression using Questionnaire Star, with data analysis performed using SPSS25.0 and AMOS 24.0.
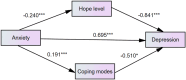
Results: The qualitative analysis identified three major themes and nine categories as key risk factors influencing the onset of adolescent depression. Three major themes were generated: school factors, family factors, and other factors. Nine categories were generated: heavy academic load, strained peer, and teacher-student relationships; unstable family structures, internal familial conflicts, and high parental expectations; a strong sense of social isolation, insufficient sexual education, and prevalent suicidal ideation or attempts. A nurturing and supportive school environment significantly bolsters adolescents' sense of hope and coping abilities, while a warm and encouraging family setting effectively mitigates psychological stress. Conversely, heightened loneliness and the onset of suicidal ideation are frequently linked to diminished hope and the adoption of maladaptive coping strategies. Hence, to comprehensively understand the intricate interplay of these factors, this study concentrated on the levels of hope and coping mechanisms, investigating their potential mediating role in adolescent anxiety and depression. Quantitative analysis revealed a positive correlation between anxiety and depression (r = 0.767, p<0.01). Additionally, it was found that hope levels and coping strategies mediated the relationship between anxiety and depressive symptoms (β = -0.24-0.84 = 0.20, p < 0.001; β = 0.19-0.51 = -0.10, p < 0.01), with the mediating influence of hope levels being more significant than that of coping strategies.
Conclusion: Enhancing hope levels and fostering positive coping strategies are instrumental in aiding adolescents with depression to alleviate their anxiety and depressive symptoms. Moreover, this study underscored the importance of focusing on adolescents' mental health and providing them with emotional support, thereby increasing their hope levels and encouraging the adoption of positive coping mechanisms to effectively address their challenges.
Keywords: Adolescent patients; Anxiety; Coping modes; Depression; Hope level.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Gaynes Lux, Gartlehner, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress. Anxiety. 2020;372:134–145. - PubMed
-
- Tiirikainen Haravuori, Ranta, et al. Psychometric properties of the 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7) in a large representative sample of Finnish adolescents. Psychiatr. Res. 2019;272:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Lu Adolescent depression: national trends, risk factors, and healthcare disparities. Am. J. Health Behav. 2019;431:181–194. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources