Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Lung Transplantation: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Armamentarium in a 21st Century Perspective
- PMID: 39170865
- PMCID: PMC11336419
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2024.12973
Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Lung Transplantation: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Armamentarium in a 21st Century Perspective
Abstract
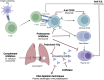
Humoral immunity is a major waypoint towards chronic allograft dysfunction in lung transplantation (LT) recipients. Though allo-immunization and antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) are well-known entities, some diagnostic gaps need to be addressed. Morphological analysis could be enhanced by digital pathology and artificial intelligence-based companion tools. Graft transcriptomics can help to identify graft failure phenotypes or endotypes. Donor-derived cell free DNA is being evaluated for graft-loss risk stratification and tailored surveillance. Preventative therapies should be tailored according to risk. The donor pool can be enlarged for candidates with HLA sensitization, with strategies combining plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin and immune cell depletion, or with emerging or innovative therapies such as imlifidase or immunoadsorption. In cases of insufficient pre-transplant desensitization, the effects of antibodies on the allograft can be prevented by targeting the complement cascade, although evidence for this strategy in LT is limited. In LT recipients with a humoral response, strategies are combined, including depletion of immune cells (plasmapheresis or immunoadsorption), inhibition of immune pathways, or modulation of the inflammatory cascade, which can be achieved with photopheresis. Altogether, these innovative techniques offer promising perspectives for LT recipients and shape the 21st century's armamentarium against AMR.
Keywords: antibody-mediated rejection; diagnosis; diagnosis biomarker; lung transplantation; therapeutic approaches.
Copyright © 2024 Messika, Belousova, Parquin and Roux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials