Progressive trends on the application of artificial neural networks in animal sciences - A review
- PMID: 39170908
- PMCID: PMC11334143
- DOI: 10.17221/45/2021-VETMED
Progressive trends on the application of artificial neural networks in animal sciences - A review
Abstract
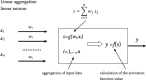
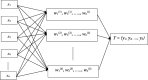
In recent years, artificial neural networks have become the subject of intensive research in a number of scientific areas. The high performance and operational speed of neural models open up a wide spectrum of applications in various areas of life sciences. Objectives pursued by many scientists, who use neural modelling in their research, focus - among others - on intensifying real-time calculations. This study shows the possibility of using Multilayer-Perceptron (MLP) and Radial Basis Function (RBF) models of artificial neural networks for the future development of new methods for animal science. The process should be explained explicitly to make the MLP and RBF models more readily accepted by more researchers. This study describes and recommends certain models as well as uses forecasting methods, which are represented by the chosen neural network topologies, in particular MLP and RBF models for more successful operations in the field of animals sciences.
Keywords: livestock animal science; machine learning; machine models.
Copyright: © 2022 Bauer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A review of recent developments in the application of machine learning in solar thermal collector modelling.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jan;30(2):2406-2439. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24044-y. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36399296 Review.
-
Predicting centre of mass horizontal speed in low to severe swimming intensities with linear and non-linear models.J Sports Sci. 2019 Jul;37(13):1512-1520. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2019.1574949. Epub 2019 Feb 6. J Sports Sci. 2019. PMID: 30724700
-
Exergetic performance prediction of solar air heater using MLP, GRNN and RBF models of artificial neural network technique.J Environ Manage. 2018 Oct 1;223:566-575. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.06.033. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Environ Manage. 2018. PMID: 29975883
-
Artificial neural networks applied to forecasting time series.Psicothema. 2011 Apr;23(2):322-9. Psicothema. 2011. PMID: 21504688
-
Machine Learning-Enabled NIR Spectroscopy. Part 2: Workflow for Selecting a Subset of Samples from Publicly Accessible Data.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Jan 10;24(1):34. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02493-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 36627410 Review.
References
-
- Adamczyk K, Molenda K, Szarek J, Skrzynski GC. Prediction of bulls’ slaughter value from growth data using artificial neural network. J Cen Euro Agric. 2005;6(2):133-42.
-
- Alsmadi S, Omar B, Noah A. Back propagation algorithm: The best algorithm among the multi-layer perceptron algorithm. J Comp Sci Net Security. 2009;9(4):378-83.
-
- Amit D. Modeling brain functions: The world of attractor neural networks. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1989. 504 p.
-
- Anderson JA, Rosenfeld E. Neurocomputing – Foundations of research. Cambridge (Mass), London (GB): MIT Press; 1988. 729 p.
-
- Aruwayo A, Ahmed Ks, Muhammad IR. Ruminant production and nutrition chemical composition of some selected non-conventional feed resources katsina. 8th Asan-Nias Joint Annual Meeting; Sep 8-12; 2020; p. 1096-8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
