Omics approaches in asthma research: Challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 39170962
- PMCID: PMC11332849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pccm.2024.02.002
Omics approaches in asthma research: Challenges and opportunities
Abstract
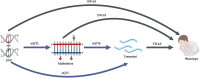
Asthma, a chronic respiratory disease with a global prevalence of approximately 300 million individuals, presents a significant societal and economic burden. This multifaceted syndrome exhibits diverse clinical phenotypes and pathogenic endotypes influenced by various factors. The advent of omics technologies has revolutionized asthma research by delving into the molecular foundation of the disease to unravel its underlying mechanisms. Omics technologies are employed to systematically screen for potential biomarkers, encompassing genes, transcripts, methylation sites, proteins, and even the microbiome components. This review provides an insightful overview of omics applications in asthma research, with a special emphasis on genetics, transcriptomics, epigenomics, and the microbiome. We explore the cutting-edge methods, discoveries, challenges, and potential future directions in the realm of asthma omics research. By integrating multi-omics and non-omics data through advanced statistical techniques, we aspire to advance precision medicine in asthma, guiding diagnosis, risk assessment, and personalized treatment strategies for this heterogeneous condition.
Keywords: Asthma; Epigenomics; Genomics; Metagenomics; Multi-omics integration; Transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2022. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org/. [Last accessed on January 2, 2024].
-
- Network GA. Auckland; New Zealand: 2018. The Global Asthma Report.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

