Evaluation of the protective effect of Curcuma longa and PPARγ agonist, pioglitazone on paraquat-induced lung injury in rats
- PMID: 39172009
- PMCID: PMC11340013
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.70001
Evaluation of the protective effect of Curcuma longa and PPARγ agonist, pioglitazone on paraquat-induced lung injury in rats
Abstract
Background: The inhalation of paraquat (PQ), one of the most widely used herbicides in the world, can result in lung injury. Curcuma longa (Cl) has long history in traditional and folk medicine for the treatment of a wide range of disorders including respiratory diseases.
Aim: The aim of the present work was to evaluate the preventive effect of Cl on inhaled PQ-induced lung injury in rats.
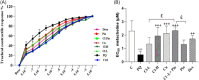
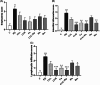
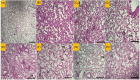
Methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into 8 groups (n = 7), one group exposed to saline (control) and other groups exposed to PQ aerosol. Saline (PQ), Cl extract, (two doses), curcumin (Cu), pioglitazone (Pio), and the combination of Cl-L + Pio and dexamethasone (Dex) were administered during the exposure period to PQ. Total and differential white blood cell (WBC) counts, oxidant and antioxidant indicators in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BALF), interleukin (IL)-10, and tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-α) levels in the lung tissues, lung histologic lesions score, and air way responsiveness to methacholine were evaluated.
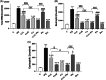
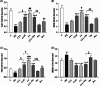
Results: WBC counts (Total and differential), malondialdehyde level, tracheal responsiveness (TR), IL-10, TNF-α and histopathological changes of the lung were markedly elevated but total thiol content and the activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase were decreased in the BALF in the PQ group. Both doses of Cl, Cu, Pio, Cl-L + Pio, and Dex markedly improved all measured variables in comparison with the PQ group.
Conclusion: CI, Pio, and Cl-L + Pio improved PQ-induced lung inflammation and oxidative damage comparable with the effects of Dex.
Keywords: Curcuma longa; inflammation; lung injury; oxidative stress; paraquat.
© 2024 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
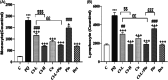
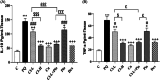
Similar articles
-
The preventive effectiveness of Crocus sativus extract in treating lung injuries caused by inhaled paraquat in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 1):118767. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118767. Epub 2024 Sep 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39236778
-
Paraquat-induced systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in rats improved by Curcuma longa ethanolic extract, curcumin and a PPAR agonist.Toxicon. 2023 May;227:107090. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2023.107090. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Toxicon. 2023. PMID: 36965712
-
Evaluation of nano-curcumin against inhaled paraquat-induced lung injury in rats.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Jun;75(3):671-681. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00483-3. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37039972
-
Systemic inflammation and oxidative stress induced by inhaled paraquat in rat improved by carvacrol, possible role of PPARγ receptors.Biofactors. 2021 Sep;47(5):778-787. doi: 10.1002/biof.1761. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Biofactors. 2021. Retraction in: Biofactors. 2024 Jul-Aug;50(4):863. doi: 10.1002/biof.2093. PMID: 34089284 Retracted.
-
Experimental and clinical reports on anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of Curcuma longa and curcumin, an updated and comprehensive review.Biofactors. 2021 May;47(3):311-350. doi: 10.1002/biof.1716. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33606322 Review.
References
-
- Walsh A, Kingwell R. Economic implications of the loss of glyphosate and paraquat on Australian mixed enterprise farms. Agricult Sys. 2021;193:103207.
-
- Deroco PB, Wachholz Junior D, Kubota LT. Silver Inkjet‐Printed electrode on paper for electrochemical sensing of paraquat. Chemosensors. 2021;9(4):61.
-
- Marambe B, Herath S. Banning of herbicides and the impact on agriculture: the case of glyphosate in Sri Lanka. Weed Sci. 2020;68(3):246‐252.
-
- Wang T, Ou L, Li X, et al. Inhibition of Galectin‐3 attenuates silica particles‐induced silicosis via regulating the GSK‐3β/β‐catenin signal pathway‐mediated epithelial‐mesenchymal transition. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;368:110218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

