MerTK-dependent efferocytosis by monocytic-MDSCs mediates resolution of ischemia/reperfusion injury after lung transplant
- PMID: 39172530
- PMCID: PMC11466183
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.179876
MerTK-dependent efferocytosis by monocytic-MDSCs mediates resolution of ischemia/reperfusion injury after lung transplant
Abstract
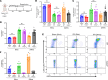
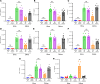
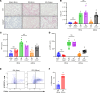
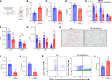
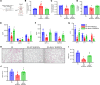
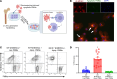
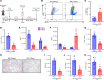
Lung transplantation (LTx) outcomes are impeded by ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) and subsequent chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD). We examined the undefined role of receptor Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK) on monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSCs) in efferocytosis to facilitate resolution of lung IRI. Single-cell RNA sequencing of lung tissue and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from patients after LTx were analyzed. Murine lung hilar ligation and allogeneic orthotopic LTx models of IRI were used with BALB/c (WT), Cebpb-/- (MDSC-deficient), Mertk-/-, or MerTK-cleavage-resistant mice. A significant downregulation in MerTK-related efferocytosis genes in M-MDSC populations of patients with CLAD was observed compared with healthy individuals. In the murine IRI model, a significant increase in M-MDSCs, MerTK expression, and efferocytosis and attenuation of lung dysfunction was observed in WT mice during injury resolution that was absent in Cebpb-/- and Mertk-/- mice. Adoptive transfer of M-MDSCs in Cebpb-/- mice significantly attenuated lung dysfunction and inflammation. Additionally, in a murine orthotopic LTx model, increases in M-MDSCs were associated with resolution of lung IRI in the transplant recipients. In vitro studies demonstrated the ability of M-MDSCs to efferocytose apoptotic neutrophils in a MerTK-dependent manner. Our results suggest that MerTK-dependent efferocytosis by M-MDSCs can substantially contribute to the resolution of post-LTx IRI.
Keywords: Immunology; Innate immunity; Monocytes; Surgery; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
MerTK-dependent efferocytosis by monocytic-MDSCs mediates resolution of post-lung transplant injury.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 23:2024.01.18.576261. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.18.576261. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: JCI Insight. 2024 Aug 22;9(19):e179876. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.179876. PMID: 38328174 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Chambers DC, et al. The international thoracic organ transplant registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; focus theme: donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38(10):1042–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

