Lipid-associated macrophages' promotion of fibrosis resolution during MASH regression requires TREM2
- PMID: 39172787
- PMCID: PMC11363294
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2405746121
Lipid-associated macrophages' promotion of fibrosis resolution during MASH regression requires TREM2
Abstract
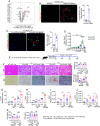
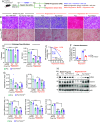
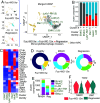
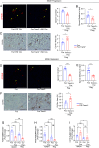
While macrophage heterogeneity during metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) has been described, the fate of these macrophages during MASH regression is poorly understood. Comparing macrophage heterogeneity during MASH progression vs regression, we identified specific macrophage subpopulations that are critical for MASH/fibrosis resolution. We elucidated the restorative pathways and gene signatures that define regression-associated macrophages and establish the importance of TREM2+ macrophages during MASH regression. Liver-resident Kupffer cells are lost during MASH and are replaced by four distinct monocyte-derived macrophage subpopulations. Trem2 is expressed in two macrophage subpopulations: i) monocyte-derived macrophages occupying the Kupffer cell niche (MoKC) and ii) lipid-associated macrophages (LAM). In regression livers, no new transcriptionally distinct macrophage subpopulation emerged. However, the relative macrophage composition changed during regression compared to MASH. While MoKC was the major macrophage subpopulation during MASH, they decreased during regression. LAM was the dominant macrophage subtype during MASH regression and maintained Trem2 expression. Both MoKC and LAM were enriched in disease-resolving pathways. Absence of TREM2 restricted the emergence of LAMs and formation of hepatic crown-like structures. TREM2+ macrophages are functionally important not only for restricting MASH-fibrosis progression but also for effective regression of inflammation and fibrosis. TREM2+ macrophages are superior collagen degraders. Lack of TREM2+ macrophages also prevented elimination of hepatic steatosis and inactivation of HSC during regression, indicating their significance in metabolic coordination with other cell types in the liver. TREM2 imparts this protective effect through multifactorial mechanisms, including improved phagocytosis, lipid handling, and collagen degradation.
Keywords: Trem2; fibrosis; lipid associated macrophages (LAM); macrophage; steatohepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:R.L. serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Cascade Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Glympse bio, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen Inc., Lipidio, Madrigal, Neurobo, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, 89 bio, Takeda, Terns Pharmaceuticals and Viking Therapeutics. C.K.G. is a founder and member of the SAB of Asteroid Pharmaceuticals. A.E.F. is an employee and stockholder of Novo Nordisk. C.K.G. is a stockholder of Asteroid Therapeutics. R.L. is a co-founder and equity holder of LipoNexus Inc. R.L. received research grants from Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Astrazeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galectin Therapeutics, Gilead, Intercept, Hanmi, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sonic Incytes and Terns Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


References
-
- Deczkowska A., Weiner A., Amit I., The physiology, pathology, and potential therapeutic applications of the TREM2 signaling pathway. Cell 181, 1207–1217 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK130190/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK078392/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK137061 R01DK133930DK091183/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- U01 AA029019/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147835/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106419/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001444/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133930/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111866/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK137061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099205/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028550/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121378/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113592/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL147835/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 DK101737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101395/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

