Medical Costs of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Disease, South Korea, 2015-2019
- PMID: 39173659
- PMCID: PMC11346975
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3009.231448
Medical Costs of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Disease, South Korea, 2015-2019
Abstract
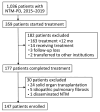
Nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD) prevalence is a rising public health concern. We assessed the long-term healthcare systems perspective of costs incurred by 147 NTM-PD patients at a tertiary hospital in South Korea. Median cumulative total medical cost in managing NTM-PD patients was US $5,044 (interquartile range US $3,586-$9,680) over 49.7 months (interquartile range 33.0-68.2 months) of follow-up. The major cost drivers were diagnostic testing and medication, accounting for 59.6% of total costs. Higher costs were associated with hospitalization for Mycobacterium abscessus infection and pulmonary comorbidities. Of the total medical care costs, 50.2% were patient co-payments resulting from limited national health insurance coverage. As South Korea faces significant problems of poverty during old age and increasing NTM-PD prevalence, the financial and socio-economic burden of NTM-PD may become a major public health concern that should be considered with regard to adequate strategies for NTM-PD patients.
Keywords: Nontuberculous mycobacteria; South Korea; bacteria; cost of illness; health expenditures; healthcare costs; pulmonary disease; tuberculosis and other mycobacteria.
Figures
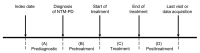

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

