Engineering Microbial Consortia as Living Materials: Advances and Prospectives
- PMID: 39174016
- PMCID: PMC11421429
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00313
Engineering Microbial Consortia as Living Materials: Advances and Prospectives
Abstract
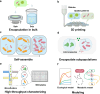
The field of Engineered Living Materials (ELMs) integrates engineered living organisms into natural biomaterials to achieve diverse objectives. Multiorganism consortia, prevalent in both naturally occurring and synthetic microbial cultures, exhibit complex functionalities and interrelationships, extending the scope of what can be achieved with individual engineered bacterial strains. However, the ELMs comprising microbial consortia are still in the developmental stage. In this Review, we introduce two strategies for designing ELMs constituted of microbial consortia: a top-down strategy, which involves characterizing microbial interactions and mimicking and reconstructing natural ecosystems, and a bottom-up strategy, which entails the rational design of synthetic consortia and their assembly with material substrates to achieve user-defined functions. Next, we summarize technologies from synthetic biology that facilitate the efficient engineering of microbial consortia for performing tasks more complex than those that can be done with single bacterial strains. Finally, we discuss essential challenges and future perspectives for microbial consortia-based ELMs.
Keywords: division of labor; engineered living materials; microbial consortia; synthetic biology toolkits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

