Cathepsin C inhibition reduces neutrophil serine protease activity and improves activated neutrophil-mediated disorders
- PMID: 39174512
- PMCID: PMC11341692
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50747-6
Cathepsin C inhibition reduces neutrophil serine protease activity and improves activated neutrophil-mediated disorders
Abstract
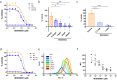
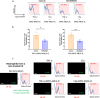
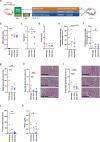
Cathepsin C (CatC) is an enzyme which regulates the maturation of neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs) essential for neutrophil activation. Activated neutrophils are key players in the innate immune system, and are also implicated in the etiology of various inflammatory diseases. This study aims to demonstrate a therapeutic potential for CatC inhibitors against disorders in which activated neutrophil-derived neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play a significant role. We demonstrate that a CatC inhibitor, MOD06051, dose-dependently suppresses the cellular activity of NSPs, including neutrophil elastase (NE), in vitro. Neutrophils derived from MOD06051-administered rats exhibit significantly lower NE activity and NET-forming ability than controls. Furthermore, MOD06051 dose-dependently ameliorates vasculitis and significantly decreases NETs when administered to a rat model of myeloperoxidase (MPO)-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV). These findings suggest that CatC inhibition is a promising strategy to reduce neutrophil activation and improve activated neutrophil-mediated diseases such as MPO-AAV.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.S., W.S., T.N., and Y.T. are employees of Alivexis, Inc. Y.N., S.M., and A.I. were given research funds from Alivexis, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

