Loss of symmetric cell division of apical neural progenitors drives DENND5A-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy
- PMID: 39174524
- PMCID: PMC11341845
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51310-z
Loss of symmetric cell division of apical neural progenitors drives DENND5A-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy
Abstract
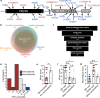
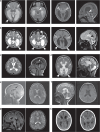
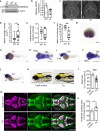
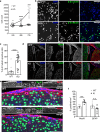
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs) feature altered brain development, developmental delay and seizures, with seizures exacerbating developmental delay. Here we identify a cohort with biallelic variants in DENND5A, encoding a membrane trafficking protein, and develop animal models with phenotypes like the human syndrome. We demonstrate that DENND5A interacts with Pals1/MUPP1, components of the Crumbs apical polarity complex required for symmetrical division of neural progenitor cells. Human induced pluripotent stem cells lacking DENND5A fail to undergo symmetric cell division with an inherent propensity to differentiate into neurons. These phenotypes result from misalignment of the mitotic spindle in apical neural progenitors. Cells lacking DENND5A orient away from the proliferative apical domain surrounding the ventricles, biasing daughter cells towards a more fate-committed state, ultimately shortening the period of neurogenesis. This study provides a mechanism for DENND5A-related DEE that may be generalizable to other developmental conditions and provides variant-specific clinical information for physicians and families.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.M. and R.P. are employed by GeneDx, LLC. All other authors report no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Loss of symmetric cell division of apical neural progenitors drives DENND5A-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 31:2022.08.23.22278845. doi: 10.1101/2022.08.23.22278845. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 22;15(1):7239. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51310-z. PMID: 38352438 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HG007943/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Office of Strategic Coordination (OSC)
- UM1 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS105078/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- NS105078/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- HG011758/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- OGI-147/Ontario Genomics Institute (OGI)
- U01 HG007943/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS134350/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 57166498/Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (German Academic Exchange Service)
- U01 HG011758/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

