Development and validation of a nomogram based on Lasso-Logistic regression for predicting splenomegaly secondary to acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 39174911
- PMCID: PMC11340059
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03331-7
Development and validation of a nomogram based on Lasso-Logistic regression for predicting splenomegaly secondary to acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Purpose: Investigate the clinical characteristics of splenomegaly secondary to acute pancreatitis (SSAP) and construct a nomogram prediction model based on Lasso-Logistic regression.
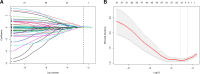
Methods: A retrospective case-control study was conducted to analyze the laboratory parameters and computed tomography (CT) imaging of acute pancreatitis (AP) patients recruited at Xuanwu Hospital from December 2014 to December 2021. Lasso regression was used to identify risk factors, and a novel nomogram was developed. The performance of the nomogram in discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness was evaluated through internal validation.
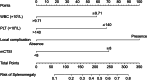
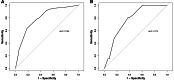
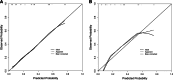
Results: The prevalence of SSAP was 9.2% (88/950), with the first detection occurring 65(30, 125) days after AP onset. Compared with the control group, the SSAP group exhibited a higher frequency of persistent respiratory failure, persistent renal failure, infected pancreatic necrosis, and severe AP, along with an increased need for surgery and longer hospital stay (P < 0.05 for all). There were 185 and 79 patients in the training and internal validation cohorts, respectively. Variables screened by Lasso regression, including platelet count, white blood cell (WBC) count, local complications, and modified CT severity index (mCTSI), were incorporated into the Logistic model. Multivariate analysis showed that WBC count ≦9.71 × 109/L, platelet count ≦140 × 109/L, mCTSI ≧8, and the presence of local complications were independently associated with the occurrence of SSAP. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.790. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed that the model had good fitness (P = 0.954). Additionally, the nomogram performed well in the internal validation cohorts.
Conclusions: SSAP is relatively common, and patients with this condition often have a worse clinical prognosis. Patients with low WBC and platelet counts, high mCTSI, and local complications in the early stages of the illness are at a higher risk for SSAP. A simple nomogram tool can be helpful for early prediction of SSAP.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Lasso-Logistic regression; Nomogram; Risk factors; Splenomegaly.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and alidation of a severity prediction model for acute pancreatitis based on CT severity index: A retrospective case-control study.PLoS One. 2024 May 24;19(5):e0303684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303684. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38787912 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram for the prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis in moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis.J Dig Dis. 2024 Apr;25(4):238-247. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.13271. Epub 2024 May 23. J Dig Dis. 2024. PMID: 38779802
-
Development and validation of a risk prediction score for the severity of acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis in Chinese patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 7;28(33):4846-4860. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4846. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36156930 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Establishment and evaluation of early in-hospital death prediction model for patients with acute pancreatitis in intensive care unit].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Aug;35(8):865-869. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220713-00660. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37593868 Chinese.
-
Analysis of clinical characteristics of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome with acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2453081. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2453081. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39829396 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A risk nomogram for 30-day mortality in Chinese patients with acute pancreatitis using LASSO-logistic regression.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):17097. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02055-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379755 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in the diagnosis of biliopancreatic diseases: A comparative review and study on future insights.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):103391. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i4.103391. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40291132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boxhoorn L, Voermans RP, Bouwense SA, et al. Acute pancreatitis. Am Gastroenterol Assoc Inst Guidel Initial Manage. 2020;396(10252):726–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

