Comparison of the efficacy of Er,Cr:YSGG laser on oral biofilm removal from implant surfaces with various application times for the treatment of peri-implantitis defects: ex vivo study
- PMID: 39174958
- PMCID: PMC11342501
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04698-5
Comparison of the efficacy of Er,Cr:YSGG laser on oral biofilm removal from implant surfaces with various application times for the treatment of peri-implantitis defects: ex vivo study
Abstract
Purpose: The major struggle in peri-implantitis therapy is the availability of successful decontamination of the infected implant surface. The main hypothesis of this study was the Er,Cr: YSGG laser decontamination efficacy investigation on the infected implant surfaces with various peri-implantitis defects. The primary objective of this study was to decide the efficacy of Er,Cr:YSGG laser as a decontamination tool at various peri-implantitis simulating defects. The secondary objective was to compare the efficacy of the Er,Cr: YSGG laser on oral biofilm removal between two protocols the first protocol (4 cycles at 2.5 min) and the second protocol (5 cycles at 5 min) at various peri-implantitis simulating defects.
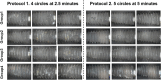
Materials and methods: A total of 3 subjects whose plaque biofilms formed in-vivo on twenty-four tested implants were divided into four tested groups. Two native implants were tested as controls.The in vitro defect model was computer-aided designed and printed into a 3D-printed model with various anulations in peri-implant infrabony defects, which were 15,30,60,and 90 degrees.
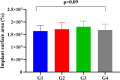
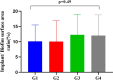
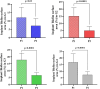
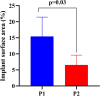
Results: Both Er, Cr: YSGG decontamination protocols at 50 mJ (1.5 W/30 Hz), 50% air, and 40% water were effective at reducing the total implant surface area/ biofilm ratio (%), but the second protocol had a markedly greater reduction in the duration of application (5 cycles at 5 min) than did the first protocol (4 cycles at 2.5 min).
Conclusion: The Er, Cr: YSGG laser is an effective decontamination device in various peri-implantitis defects. The second protocol(5 cycles at 5 min) with greater application time and circles is more effective than the first one. The defect angulation influence the decontamination capability in peri-implantitis therapy.
Clinical relevance (scientific rationale for study): Clinicians anticipate that the exploration of suitable therapeutic modalities for peri-implantitis therapy is limited by the obvious heterogeneity of the available evidence in the literature and need for a pre-clinical theoretical basis setup. The major challenges associated with peri-implantitis therapy include the successful decontamination of the infected implant surface, the absence of any damage to the treated implant surface with adequate surface roughness, and the biocompatibility of the implant surface, which allows osteoblastic cells to grow on the treated surface and is the key for successful re-osseointegration. Therefore, these are the expected empirical triads that need to be respected for successful peri-implantitis therapy. Failure of one of the triads represents a peri-implantitis therapeutic failure. The Er, Cr: YSGG laser is regarded as one of the expected devices for achieving the required triad.
Trial registration: "Efficacy of Er,Cr YSGG Laser in Treatment of Peri-implantitis".
Clinicaltrials: gov ID NCT05137821. First Posted date: 30 -11-2021.
Keywords: 3D-printed model; Biofilm removal; Decontamination efficacy; Er; Er,Cr: YSGG laser; Infrabony defects; Peri-implantitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of mechanical/physical approaches for implant surface decontamination in non-surgical submarginal instrumentation of peri-implantitis. A systematic review.J Clin Periodontol. 2023 Jun;50 Suppl 26:188-211. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13762. Epub 2023 Jan 23. J Clin Periodontol. 2023. PMID: 36550060
-
Treatment of peri-implantitis: what interventions are effective? A Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012;5 Suppl:S21-41. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012. PMID: 22834392
-
Adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for treating periodontal and peri-implant diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 12;7(7):CD011778. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011778.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38994711 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different types of dental implants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 22;(7):CD003815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003815.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25048469
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: treatment of peri-implantitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1(1):CD004970. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004970.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258958 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Disinfection Efficacy of Er-YAG Laser Light on Single-Species Candida Biofilms: Systematic Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 19;13(4):942. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040942. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berglundh T, Armitage G, Araujo MG, et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions. J Periodontol. 2018;89(March):S313–8. 10.1002/JPER.17-0739. 10.1002/JPER.17-0739 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jaramillo RAM, Giraldo AV, Duque AD, Aristizabal AG, Giraldo VM. Guía De Práctica Clínica Para La Prevención Y El Tratamiento De enfermedades periimplantares. Rev Fac Odontol. 2019;31(1–2):6–25. 10.17533/udea.rfo.v31n1-2a1.10.17533/udea.rfo.v31n1-2a1 - DOI
-
- Monje A, Amerio E, Cha JK, et al. Strategies for implant surface decontamination in peri-implantitis therapy. Int J oral Implantol (Berlin, Ger). 2022;15(3):213–48. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36082658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

