Characterization of two melanoma cell lines resistant to BRAF/MEK inhibitors (vemurafenib and cobimetinib)
- PMID: 39175042
- PMCID: PMC11342534
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01788-3
Characterization of two melanoma cell lines resistant to BRAF/MEK inhibitors (vemurafenib and cobimetinib)
Abstract
Background: BRAF (v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1)/MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase) inhibitors are used for melanoma treatment. Unfortunately, patients treated with this combined therapy develop resistance to treatment quite quickly, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are not yet fully understood. Here, we report and characterize two melanoma cell lines (WM9 and Hs294T) resistant to BRAF (vemurafenib) and MEK (cobimetinib) inhibitors.
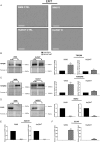
Methods: Cell viability was assessed via the XTT test. The level of selected proteins as well as activation of signaling pathways were evaluated using Western blotting. The expression of the chosen genes was assessed by RT-PCR. The distribution of cell cycle phases was analyzed by flow cytometry, and confocal microscopy was used to take photos of spheroids. The composition of cytokines secreted by cells was determined using a human cytokine array.
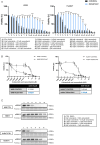
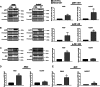
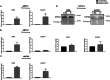
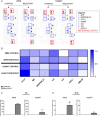
Results: The resistant cells had increased survival and activation of ERK kinase in the presence of BRAF/MEK inhibitors. The IC50 values for these cells were over 1000 times higher than for controls. Resistant cells also exhibited elevated activation of AKT, p38, and JNK signaling pathways with increased expression of EGFR, ErbB2, MET, and PDGFRβ receptors as well as reduced expression of ErbB3 receptor. Furthermore, these cells demonstrated increased expression of genes encoding proteins involved in drug transport and metabolism. Resistant cells also exhibited features of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells as well as reduced proliferation rate and elevated cytokine secretion.
Conclusions: In summary, this work describes BRAF/MEK-inhibitor-resistant melanoma cells, allowing for better understanding the underlying mechanisms of resistance. The results may thus contribute to the development of new, more effective therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: BRAFi/MEKi; Cobimetinib; Drug resistance; Melanoma; Targeted therapy; Vemurafenib.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Hartman RI, Lin JY. Cutaneous Melanoma-A Review in Detection, Staging, and Management. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:25–38. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30497675/. Cited 2024 May 29. - PubMed
-
- Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, Zanghì A, Spandidos DA, Mccubrey JA et al. Cutaneous melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review). Int J Oncol; 2018;52:1071–80. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29532857/. Cited 2024 May 29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Subbiah V, Baik C, Kirkwood JM. Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations. Trends Cancer; 2020;6:797–810. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32540454/. Cited 2024 May 29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

