Evaluation of targeted sequencing for pathogen identification in bone and joint infections: a cohort study from China
- PMID: 39175046
- PMCID: PMC11342589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-024-00733-z
Evaluation of targeted sequencing for pathogen identification in bone and joint infections: a cohort study from China
Abstract
Purpose: Bone and joint tuberculosis (BJTB) is a distinct variant of tuberculosis in which clinical diagnosis often leads to relative misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the targeted nanopore sequencing (TNPseq) assay for BJTB patients in China.
Method: The study enrolled a cohort of 163 patients with suspected BJTB. Diagnostic testing was performed using the TNPseq assay on samples including punctured tissue, pus, and blood. The diagnostic accuracy of the TNPseq assay was then compared with that of the T-SPOT and Xpert MTB/RIF assays.
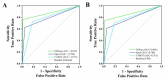
Result: TNPseq exhibited superior performance in terms of accuracy, demonstrating a sensitivity of 76.3% (95% CI: 71.0-81.6%) and a specificity of 98.8% (95% CI: 93.5-100%) in clinical diagnosis. When evaluated against a composite reference standard, TNPseq demonstrated a sensitivity of 74.4% (95% CI: 69.3-79.5%) and a specificity of 98.8% (95% CI: 93.7-100%). These results exceed the performance of both the T-SPOT and Xpert MTB/RIF tests. Notably, TNPseq demonstrated high specificity and accuracy in puncture specimens, with a sensitivity of 75.0% (95% CI: 70.2-79.8%) and a specificity of 98.3% (95% CI: 92.7-100%), as well as in pus samples, with a sensitivity of 83.3% (95% CI: 78.6-88.1%) and a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 100-100%). Additionally, TNPseq facilitated the detection of mixed infection scenarios, identifying 20 cases of bacterial-fungal co-infection, 17 cases of bacterial-viral co-infection, and two cases of simultaneous bacterial-fungal-viral co-infection.
Conclusion: TNPseq demonstrated great potential in the diagnosis of BJTB due to its high sensitivity and specificity. The ability of TNPseq to diagnose pathogens and detect drug resistance genes can also guide subsequent treatment. Expanding the application scenarios and scope of TNPseq will enable it to benefit more clinical treatments.
Keywords: Bone and joint; Diagnosis; Infection; Targeted nanopore sequencing; Tuberculosis; Xpert MTB/RIF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative study on the value of Xpert MTB/RIF and T-SPOT.TB tests in the diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Jan;500:115-119. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.026. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31654631
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for bone and joint tuberculosis using tissue specimens.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;105:224-229. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.030. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33582371
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and GenoType MTBDRplus assays for the rapid diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis.Int J Infect Dis. 2015 Jul;36:27-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 May 21. Int J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26004172
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra assays for screening for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults, irrespective of signs or symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 23;3(3):CD013694. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013694.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33755189 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculosis disease: A preliminary systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jan;90:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.09.016. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31546008
Cited by
-
Clinical application of targeted nanopore sequencing in pathogen detection in patients with sepsis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 24;25(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10604-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39994600 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends in the application of nanopore sequencing technology in the detection of infectious disease pathogens: a bibliometric analysis from 2014 to 2024.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 23;12:1610063. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1610063. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40771470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 05.014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

