Toward the latest advancements in cardiac regeneration using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) technology: approaches and challenges
- PMID: 39175068
- PMCID: PMC11342568
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05499-8
Toward the latest advancements in cardiac regeneration using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) technology: approaches and challenges
Abstract
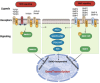
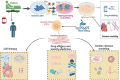
A novel approach to treating heart failures was developed with the introduction of iPSC technology. Knowledge in regenerative medicine, developmental biology, and the identification of illnesses at the cellular level has exploded since the discovery of iPSCs. One of the most frequent causes of mortality associated with cardiovascular disease is the loss of cardiomyocytes (CMs), followed by heart failure. A possible treatment for heart failure involves restoring cardiac function and replacing damaged tissue with healthy, regenerated CMs. Significant strides in stem cell biology during the last ten years have transformed the in vitro study of human illness and enhanced our knowledge of the molecular pathways underlying human disease, regenerative medicine, and drug development. We seek to examine iPSC advancements in disease modeling, drug discovery, iPSC-Based cell treatments, and purification methods in this article.
Keywords: Cardiac regeneration; Regenerative medicine; Signaling pathways; Stem cell-based therapy; iPSC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fathi E, Farahzadi R. Mesenchymal stem cells as a cell-based therapeutic strategy targeting the telomerase activity of KG1 Acute myeloid leukemia cells. Acta Medica Iranica. 2022;60(2 SE–Articles). 10.18502/acta.v60i2.8817.
-
- Fathi E, Azarbad S, Farahzadi R, Javanmardi S, Vietor I. Effect of rat bone marrow derived-mesenchymal stem cells on Granulocyte differentiation of mononuclear cells as Preclinical Agent in Cellbased Therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2022;22(2):152–61. 10.2174/1566523221666210519111933. 10.2174/1566523221666210519111933 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

