ORIC-101, a Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, in Combination with Nab-Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors
- PMID: 39177285
- PMCID: PMC11396014
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0115
ORIC-101, a Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, in Combination with Nab-Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors
Abstract
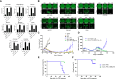
Purpose: In preclinical models, glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling drives resistance to taxane chemotherapy in multiple solid tumors via upregulation of antiapoptotic pathways. ORIC-101 is a potent and selective GR antagonist that was investigated in combination with taxane chemotherapy as an anticancer regimen preclinically and in a phase 1 clinical trial.
Patients and methods: The ability of ORIC-101 to reverse taxane resistance was assessed in cell lines and xenograft models, and a phase 1 study (NCT03928314) was conducted in patients with advanced solid tumors to determine the dose, safety, and antitumor activity of ORIC-101 with nab-paclitaxel.
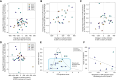
Results: ORIC-101 reversed chemoprotection induced by glucocorticoids in vitro and achieved tumor regressions when combined with paclitaxel in both taxane-naïve and -resistant xenograft models. In the phase 1 study, 21 patients were treated in dose escalation and 62 patients were treated in dose expansion. All patients in dose expansion had previously progressed on a taxane-based regimen. In dose escalation, five objective responses were observed. A preplanned futility analysis in dose expansion showed a 3.2% (95% confidence interval, 0.4-11.2) objective response rate with a median progression-free survival of 2 months (95% confidence interval, 1.8-2.8) across all four cohorts, leading to study termination. Pharmacodynamic analysis of tissue and plasma showed GR pathway downregulation in most patients in cycle 1.
Conclusions: ORIC-101 with nab-paclitaxel showed limited clinical activity in taxane-resistant solid tumors. Despite clear inhibition of GR pathway signaling, the insufficient clinical signal underscores the challenges of targeting a single resistance pathway when multiple mechanisms of resistance may be in play.
Significance: Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) upregulation is a mechanism of resistance to taxane chemotherapy in preclinical cancer models. ORIC-101 is a small molecule GR inhibitor. In this phase 1 study, ORIC-101 plus nab-paclitaxel did not show meaningful clinical benefit in patients who previously progressed on taxanes despite successful GR pathway downregulation.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.T. Chen reports grants from Oric Pharmaceuticals during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Boxer Capital and Guidepoint Global, grants from ADC Therapeutiucs, Gilead Sciences, Kinnate Biopharma, Mersana Therapeutics, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, Rain Oncology, Riboscience, D3 Bio, Takeda, Revolution Medicines, and Tango Therapeutics outside the submitted work. S. Kummar reports other from Bayer, Springworks Therapeutics, Mirati, Mundibiopharma, XYOne Therapeutics, GI Innovations, HarbourBiomed, BPGbio Therapeutics, Genome and Company, Oxford Biotherapeutics, Gilead, Genome Insight, and Fortress Biotech, Inc. outside the submitted work; and PathomIQ (co-founder), Arxeon (co-founder spouse). A.W. Tolcher reports personal fees and other from ABBVIE, Inc., Aclaris Therapeutics, Affinia Therapeutics, Inc., AGENUS, Inc., ASANA BIOSCIENCES, ASCENTAGE, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Axlmmune, Bayer, Blu Print Oncology, Coretag Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Exelixis, Inc., FibroGen, GILDE HEALTHCARE PARTNERS, HBM PARTNERS, IDEA Pharma, Ikena Oncology, Immuneering, Immunomet Therapeutics, Inc., Impact Therapeutics US, Inc., Karma Oncology B.V., Kirilys Therapeutics, Inc., Lengo Therapeutics, Inc., Link Immunotherapeutics, Medicxi, Merck KGA, Mekanistic Therapeutics, Menarini Ricerche, Mersana, NANOBIOTIX, Nerviano Medical Sciences S.r.I. (NMS), Novo Nordisk Inc., Novo Ventures, Nurix Therapeutics, Ocellaris Pharma, Inc. & Eli Lilly, Partner Therapeutics, Pfizer Inc., PIERRE FABRE, Praxia Precision Medicines, PYRAMID BIOSCIENCES, Qualigen Therapeutics, Roche, RYVU THERAPEUTICS, Seattle Genetics, Singzyme Pte Ltd., SK Life Science, SOTIO Biotechnology Co., Senti Biosciences, Sun Pharma Advanced Research Company (SPARC), TheraTechnologies, Transcenta Therapeutics Inc., Transgene, Trillium Therapeutics Inc., TUBULIS, Venus Oncology, Verastem Oncology, and VIDA VENTURES ADVISORS, LLC during the conduct of the study; ABBVIE, Inc., Aclaris Therapeutics, Affinia Therapeutics, Inc., AGENUS, Inc., ASANA BIOSCIENCES, ASCENTAGE, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Axlmmune, Bayer, Blu Print Oncology, Coretag Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Exelixis, Inc., FibroGen, GILDE HEALTHCARE PARTNERS, HBM PARTNERS, IDEA Pharma, Ikena Oncology, Immuneering, Immunomet Therapeutics, Inc., Impact Therapeutics US, Inc., Karma Oncology B.V., Kirilys Therapeutics, Inc., Lengo Therapeutics, Inc., Link Immunotherapeutics, Medicxi, Merck KGA, Mekanistic Therapeutics, Menarini Ricerche, Mersana, NANOBIOTIX, Nerviano Medical Sciences S.r.I. (NMS), Novo Nordisk Inc., Novo Ventures, Nurix Therapeutics, Ocellaris Pharma, Inc. & Eli Lilly, Partner Therapeutics, Pfizer Inc., PIERRE FABRE, Praxia Precision Medicines, PYRAMID BIOSCIENCES, Qualigen Therapeutics, Roche, RYVU THERAPEUTICS, Seattle Genetics, Singzyme Pte Ltd., SK Life Science, SOTIO Biotechnology Co., Senti Biosciences, Sun Pharma Advanced Research Company (SPARC), TheraTechnologies, Transcenta Therapeutics Inc., Transgene, Trillium Therapeutics Inc., TUBULIS, Venus Oncology, Verastem Oncology, VIDA VENTURES ADVISORS, LLC, ADAGENE, Inc., BIOINVENT, Boeringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Bright Peak Therapeutics, Cullinan Oncology, Elucida Oncology, EMD SERONO/MERCK KGaA, HEXAGON BIO, INC., IMMUNOME, JAZZ, Leerink, MIRATI, NBE THERAPEUTICS, Nested Therapeutics, Inc., Pheon Therapeutics, PYXIS Oncology, Roche, SPARC, Spirea Limited Inc., Tagworks Pharmaceuticals, Vincerx, VRISE Therapeutics, Inc., Zentalis Pharmaceuticals, and ZielBio, Inc. outside the submitted work; in addition, A.W. Tolcher has a patent to Ascentage issued and a patent to Zentalis issued. N.T. Ueno reports Consulting roles are held with the following companies: AstraZeneca plc ($13300), Bayer AG (Pfizer Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., CytoDyn Inc., Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., DynaMed, LLC, Eisai Co., Ltd., KeChow Pharma, Inc., Lavender Health Ltd., OBI Pharma Inc., OncoCyte Co., Ourotech, Inc., DBA Pear Bio, Kirilys Therapeutics, Inc., Peptilogics, Inc., Phoenix Molecular Designs, Preferred Medicine, Inc., Puma Biotechnology, Inc., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Inc., Sysmex Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Ltd., Unitech Medical, Inc., CARNA Biosciences, Inc., ChemDiv, Inc., DualityBio, LARVOL, Oncolys BioPharma Inc., Rakuten Medical, Inc., Merck Co., AnHeart Therapeutics Inc., Carisma Therapeutics, Inc., Lilly, Inc., and Therimunex. Speaker or preceptorship roles are held with the following companies: Bristol-Myers Squibb, CareNet Inc, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Genomic Health, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Inc., and Medscape. Research agreements are in place with the following companies: AnHeart Therapeutics Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Phoenix Molecular Designs, Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Puma Biotechnology, Inc., Merck Co., Oncolys BioPharma Inc., OBI Pharma Inc., ChemDiv, Inc., Tolero Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and VITRAC Therapeutics, LLC. S.L. Davis reports other from Oric during the conduct of the study; other from BMS, Symphogen, I-Mab, TriSalus Life Sciences, Tvardi Therapeutics, EMD Serono, and Merck outside the submitted work. E. Hamilton reports grants from ORIC Pharmaceuticals during the conduct of the study; grants from Abbvie and Acerta, grants and other from Accutar Biotechnology, Arvinas, and AstraZeneca, grants from ADC Therapeutics, AKESOBIO Australia, Amgen, Aravive, ArQule, Artios, AtlasMedx, BeiGene, Black Diamond, Bliss BioPharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cascadian Therapeutics, Clovis, Compugen, Context Therapeutics, Cullinan, Curis, and CytomX, grants and other from Daiichi Sankyo, grants from Dana Farber Cancer Inst, Dantari, Deciphera, Duality Biologics, eFFECTOR Therapeutics, and Eisai, grants and other from Ellipses Pharma, Elucida Oncology, EMD Serono, Fochon Pharmaceuticals, FujiFilm, and G1 Therapeutics, grants and other from Gilead Sciences, grants from H3 Biomedicine, Harpoon, Hutchinson MediPharma, Immunogen, Immunomedics, Incyte, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inspirna, Investis Bio, Jacobio, Karyopharm, K-Group Beta, Kind Pharmaceuticals, and Leap Therapeutics, grants and other from Lilly, grants from Loxo Oncology, Lycera, Mabspace Biosciences, Macrogenics, and MedImmune, grants and other from Mersana, Merus, Millennium, Molecular Templates, Myriad Genetic Laboratories, grants and other from Novartis, and Nucana, grants and other from Olema, grants from OncoMed, Oncothyreon, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Orinove, and Orum Therapeutics, grants and other from Pfizer, grants from PharmaMar, grants from Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Pionyr Immunotherapeutics, Plexxikon, Prelude Therapeutics, Profound Bio, Radius Health, Regeneron, Relay Therapeutics, Repertoire Immune Medicine, and Rgenix, grants and other from Roche/Genentech, grants from SeaGen, Sermonix Pharmaceuticals, Shattuck Labs, Silverback Therapeutics, and StemCentRx, grants and other from Stemline Therapeutics, grants from Sutro, Syndax, Syros, Taiho, TapImmune, Tesaro, Tolmar, Torque Therapeutics, Treadwell Therapeutics, Verastem, Zenith Epigenetics, and Zymeworks, other from Circle Pharma, Entos, Fosun Pharma, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Jefferies, Johnson and Johnson, Medical Pharma Services, Tempus Labs, Theratechnologies, Tubulis, Verascity Science, and Zentalis Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. M.R. Patel reports other from ORIC during the conduct of the study; other from see
Figures
References
-
- Azher S, Azami O, Amato C, McCullough M, Celentano A, Cirillo N. The non-conventional effects of glucocorticoids in cancer. J Cell Physiol 2016;231:2368–73. - PubMed
-
- Hou WJ, Guan JH, Dong Q, Han YH, Zhang R. Dexamethasone inhibits the effect of paclitaxel on human ovarian carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2013;17:2902–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

