Survival and complication rates of tooth- and implant-supported restorations after an observation period up to 36 years
- PMID: 39177417
- PMCID: PMC11629436
- DOI: 10.1111/clr.14351
Survival and complication rates of tooth- and implant-supported restorations after an observation period up to 36 years
Abstract
Background: Tooth- and implant-supported fixed dental prostheses are well-documented and aesthetic treatment alternatives, and after a comprehensive periodontal treatment, a protocol with a good long-term prognosis if the maintenance program is strictly followed.
Aim: To reexamine a pre-existing patient cohort in order to obtain estimated long-term survival and complication outcomes of fixed dental prostheses.
Materials and methods: For this study, patients treated with fixed dental prostheses between 1978 and 2002 were reexamined between 2019 and 2020. The restorations were divided in single crowns and fixed dental prostheses supported by teeth (TSC, FPTDP) and implants (ISC, FPIDP). Survival and complication rates were obtained. Kaplan-Meier functions were used to model complication probabilities, and average hazard ratios of different strata were compared using weighted Cox regression.
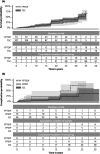
Results: The mean observation time of 40 patients and 223 reconstructions was 20.3 (±9.7, 1.2-36.2) years. The estimated survival rates were 84% (CI: 77%-92%) for TSC, 63% (CI: 51%-79%) for FPTDP, 87% (CI: 71%-100%) for ISC, and 64% (CI: 34%-100%) for FPIDP after 25 years. Biological complications included carious lesions (10.6%), periodontitis (7.9%), and peri-implantitis (6.8%). Technical complications included chipping (20.2%) and loss of retention (10.8%).
Conclusion: Biological complications lead to abutment loss in more than two-thirds of cases, regardless of the type of abutment (tooth or implant). Technical complications are less associated with abutment loss than biological complications.
Keywords: biological complications; dental implants; fixed dental prostheses; long‐term survival rates; technical complications.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Oral Implants Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures





References
-
- Aglietta, M. , Siciliano, V. I. , Zwahlen, M. , Bragger, U. , Pjetursson, B. E. , Lang, N. P. , & Salvi, G. E. (2009). A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant supported fixed dental prostheses with cantilever extensions after an observation period of at least 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 20(5), 441–451. 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01706.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bart, I. , Dobler, B. , Schmidlin, K. , Zwahlen, M. , Salvi, G. E. , Lang, N. P. , & Bragger, U. (2012). Complication and failure rates of tooth‐supported fixed dental prostheses after 7 to 19 years in function. The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 25(4), 360–367. - PubMed
-
- Berglundh, T. , Armitage, G. , Araujo, M. G. , Avila‐Ortiz, G. , Blanco, J. , Camargo, P. M. , Chen, S. , Cochran, D. , Derks, J. , Figuero, E. , Hämmerle, C. H. , Heitz‐Mayfield, L. J. A. , Huynh‐Ba, G. , Iacono, V. , Koo, K.‐T. , Lambert, F. , McCauley, L. , Quirynen, M. , Renvert, S. , … Zitzmann, N. (2018). Peri‐implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(Suppl. 20), S286–S291. 10.1111/jcpe.12957 - DOI - PubMed

