Clinical and Ultrasonographic Remission in Bio-naïve and Bio-failure Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis at 24 Weeks of Upadacitinib Treatment: The UPARAREMUS Real-Life Study
- PMID: 39177745
- PMCID: PMC11422397
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-024-00712-y
Clinical and Ultrasonographic Remission in Bio-naïve and Bio-failure Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis at 24 Weeks of Upadacitinib Treatment: The UPARAREMUS Real-Life Study
Abstract
Introduction: Clinical remission is the main target in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, several authors found synovitis in patients with RA in clinical remission at ultrasonography (US). Upadacitinib is a selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor that achieved significantly higher remission rates than adalimumab and abatacept in patients with RA. Here we present the 24-week data of the UPAdacitinib Rheumatoid Arthritis REmission UltraSonography (UPARAREMUS) study.
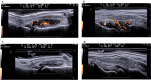
Methods: This is a longitudinal multicenter observational study, enrolling bio-naïve and bio-inadequate responder patients affected by RA. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving both clinical and US remission at week 24. The proportion of patients achieving clinical remission with different composite indexes at week 12 and 24 was also evaluated. US of four target joints (wrists and second metacarpophalangeal bilaterally) was performed at baseline and weeks 12/24, and US remission was defined as the absence of power Doppler (PD) signal ≥ 2 in one target joint, or PD ≥ 1 in two target joints.
Results: After 12 weeks and 24 weeks, 40% and 63.6% of patients achieved US plus clinical remission. The following parameters were associated with US plus clinical remission: being bio-naïve and having a shorter disease duration, although at multivariate analysis significant odds ratio (OR) was found only for being bio-naïve.
Conclusions: UPARAREMUS is the first study evaluating the efficacy of upadacitinib in reaching both clinical and US remission in patients with RA. At 24 weeks, 63.6% of patients reached the primary endpoint, the only baseline associated parameter was being bio-naïve.
Keywords: Clinical remission; JAK inhibitors; Ultrasonographic remission; Upadacitinib.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Andrea Picchianti Diamanti, Bruno Laganà, Annamaria Iagnocco, Mariasofia Cattaruzza, Marco Canzoni, Arianna D’Antonio, Maria Sole Chimenti, Simonetta Salemi, Roberta Di Rosa, Giorgio Sesti, Giandomenico Sebastiani, Chiara Scirocco, Ivan Giovannnini, Michele Maria Luchetti, Gloria Felice, Chiara De Lorenzo, Valentino Paci, Gloria Crepaldi, Bruno Frediani, Caterina Baldi, Carlo Perricone have nothing to disclose. Alen Zabotti is an Editorial Board member of
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

