Epigenetic and genetic risk of Alzheimer disease from autopsied brains in two ethnic groups
- PMID: 39177846
- PMCID: PMC11343944
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-024-02778-y
Epigenetic and genetic risk of Alzheimer disease from autopsied brains in two ethnic groups
Abstract
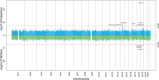
Genetic variants and epigenetic features both contribute to the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We studied the AD association of CpG-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (CGS), which act as a hub of both the genetic and epigenetic effects, in Caribbean Hispanics (CH) and generalized the findings to Non-Hispanic Whites (NHW). First, we conducted a genome-wide, sliding-window-based association with AD, in 7,155 CH and 1,283 NHW participants. Next, using data from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in 179 CH brains, we tested the cis- and trans-effects of AD-associated CGS on brain DNA methylation to mRNA expression. For the genes with significant cis- and trans-effects, we investigated their enriched pathways. We identified six genetic loci in CH with CGS dosage associated with AD at genome-wide significance levels: ADAM20 (Score = 55.19, P = 4.06 × 10-8), the intergenic region between VRTN and SYNDIG1L (Score = - 37.67, P = 2.25 × 10-9), SPG7 (16q24.3) (Score = 40.51, P = 2.23 × 10-8), PVRL2 (Score = 125.86, P = 1.64 × 10-9), TOMM40 (Score = - 18.58, P = 4.61 × 10-8), and APOE (Score = 75.12, P = 7.26 × 10-26). CGSes in PVRL2 and APOE were also significant in NHW. Except for ADAM20, CGSes in the other five loci were associated with CH brain methylation levels (mQTLs) and CGSes in SPG7, PVRL2, and APOE were also mQTLs in NHW. Except for SYNDIG1L (P = 0.08), brain methylation levels in the other five loci affected downstream mRNA expression in CH (P < 0.05), and methylation at VRTN and TOMM40 were also associated with mRNA expression in NHW. Gene expression in these six loci were also regulated by CpG sites in genes that were enriched in the neuron projection and glutamatergic synapse pathways (FDR < 0.05). DNA methylation at all six loci and mRNA expression of SYNDIG1 and TOMM40 were significantly associated with Braak Stage in CH. In summary, we identified six CpG-related genetic loci associated with AD in CH, harboring both genetic and epigenetic risks. However, their downstream effects on mRNA expression maybe ethnic specific and different from NHW.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CpG-related single nucleotide polymorphism; Epigenetics; Genetics; Hispanics; Non-Hispanic Whites.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures
Update of
-
Multi-omics Characterization of Epigenetic and Genetic Risk of Alzheimer Disease in Autopsied Brains from two Ethnic Groups.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 14:2024.02.12.24302533. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.12.24302533. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Aug 23;148(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02778-y. PMID: 38405911 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 20A22/Florida Department of Health, Ed and Ethel Moore Alzheimer Disease Research Program
- U01 AA021886/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG066107/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 8AZ06/Florida Department of Health, Ed and Ethel Moore Alzheimer Disease Research Program
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG066752/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG062517/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG062418/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

