Trained immunity is regulated by T cell-induced CD40-TRAF6 signaling
- PMID: 39178113
- PMCID: PMC11536040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114664
Trained immunity is regulated by T cell-induced CD40-TRAF6 signaling
Abstract
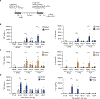
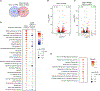
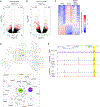
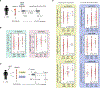
Trained immunity is characterized by histone modifications and metabolic changes in innate immune cells following exposure to inflammatory signals, leading to heightened responsiveness to secondary stimuli. Although our understanding of the molecular regulation of trained immunity has increased, the role of adaptive immune cells herein remains largely unknown. Here, we show that T cells modulate trained immunity via cluster of differentiation 40-tissue necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (CD40-TRAF6) signaling. CD40-TRAF6 inhibition modulates functional, transcriptomic, and metabolic reprogramming and modifies histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation associated with trained immunity. Besides in vitro studies, we reveal that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the proximity of CD40 are linked to trained immunity responses in vivo and that combining CD40-TRAF6 inhibition with cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4-immunoglobulin (CTLA4-Ig)-mediated co-stimulatory blockade induces long-term graft acceptance in a murine heart transplantation model. Combined, our results reveal that trained immunity is modulated by CD40-TRAF6 signaling between myeloid and adaptive immune cells and that this can be leveraged for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: CD40-CD40L; CP: Immunology; T cells; innate immunity; monocytes; nanobiologics; trained immunity.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.O., L.A.B.J., M.G.N., and W.J.M.M. declare that they are scientific founders of Trained Therapeutics Discovery.
Figures


References
-
- Quintin J, Saeed S, Martens JHA, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Ifrim DC, Logie C, Jacobs L, Jansen T, Kullberg BJ, Wijmenga C, et al. (2012). Candida albicans infection affords protection against reinfection via functional reprogramming of monocytes. Cell Host Microbe 12, 223–232. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

