In vivo pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside compound K mediated by gut microbiota
- PMID: 39178246
- PMCID: PMC11343376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307286
In vivo pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside compound K mediated by gut microbiota
Abstract
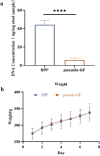
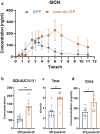
Ginsenoside Compound K (GCK) is the main metabolite of natural protopanaxadiol ginsenosides with diverse pharmacological effects. Gut microbiota contributes to the biotransformation of GCK, while the effect of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of GCK in vivo remains unclear. To illustrate the role of gut microbiota in GCK metabolism in vivo, a systematic investigation of the pharmacokinetics of GCK in specific pathogen free (SPF) and pseudo-germ-free (pseudo-GF) rats were conducted. Pseudo-GF rats were treated with non-absorbable antibiotics. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was validated for the quantification of GCK in rat plasma. Compared with SPF rats, the plasma concentration of GCK significantly increased after the gut microbiota depleted. The results showed that GCK absorption slowed down, Tmax delayed by 3.5 h, AUC0-11 increased by 1.3 times, CLz/F decreased by 0.6 times in pseudo-GF rats, and Cmax was 1.6 times higher than that of normal rats. The data indicated that gut microbiota played an important role in the pharmacokinetics of GCK in vivo.
Copyright: © 2024 Deng et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

