Enhancing RNA-lipid nanoparticle delivery: Organ- and cell-specificity and barcoding strategies
- PMID: 39179112
- PMCID: PMC11972657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.08.030
Enhancing RNA-lipid nanoparticle delivery: Organ- and cell-specificity and barcoding strategies
Abstract
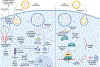
Recent advancements in RNA therapeutics highlight the critical need for precision gene delivery systems that target specific organs and cells. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as key vectors in delivering mRNA and siRNA, offering protection against enzymatic degradation, enabling targeted delivery and cellular uptake, and facilitating RNA cargo release into the cytosol. This review discusses the development and optimization of organ- and cell-specific LNPs, focusing on their design, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic applications. We explore innovations such as DNA/RNA barcoding, which facilitates high-throughput screening and precise adjustments in formulations. We address major challenges, including improving endosomal escape, minimizing off-target effects, and enhancing delivery efficiencies. Notable clinical trials and recent FDA approvals illustrate the practical applications and future potential of LNP-based RNA therapies. Our findings suggest that while considerable progress has been made, continued research is essential to resolve existing limitations and bridge the gap between preclinical and clinical evaluation of the safety and efficacy of RNA therapeutics. This review highlights the dynamic progress in LNP research. It outlines a roadmap for future advancements in RNA-based precision medicine.
Keywords: DNA barcoding; Gene delivery; Lipid carriers; Personalized medicine; RNA therapies; Site-specific.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

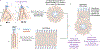




References
-
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, Perez JL, Pérez Marc G, Moreira ED, Zerbini C, Bailey R, Swanson KA, Roychoudhury S, Koury K, Li P, Kalina WV, Cooper D, Frenck RW, Hammitt LL, Türeci Ö, Nell H, Schaefer A, Ünal S, Tresnan DB, Mather S, Dormitzer PR, Şahin U, Jansen KU, Gruber WC, Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine, New England Journal of Medicine 383 (2020) 2603–2615. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, Diemert D, Spector SA, Rouphael N, Creech CB, McGettigan J, Khetan S, Segall N, Solis J, Brosz A, Fierro C, Schwartz H, Neuzil K, Corey L, Gilbert P, Janes H, Follmann D, Marovich M, Mascola J, Polakowski L, Ledgerwood J, Graham BS, Bennett H, Pajon R, Knightly C, Leav B, Deng W, Zhou H, Han S, Ivarsson M, Miller J, Zaks T, Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, New England Journal of Medicine 384 (2020) 403–416. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

