Prevalence and associations of chronic kidney disease among antiretroviral therapy-naïve persons living with HIV in Lagos, Nigeria
- PMID: 39179963
- PMCID: PMC11344324
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03711-x
Prevalence and associations of chronic kidney disease among antiretroviral therapy-naïve persons living with HIV in Lagos, Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects almost 10% of the global populace including people living with HIV (PLWH). PLWH acquire CKD from both traditional and HIV-specific CKD risk factors. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of CKD and associated factors among antiretroviral therapy (ART) naïve PLWH in Lagos, Nigeria. METHODS: This is a secondary data analysis among adult (≥ 18 years) ART-naïve PLWH enrolled at a large ART clinic in Lagos over 6 years. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) below 60ml/min/1.73m2 over 3 months. Three estimators [Body surface area corrected Cockcroft Gault (BSA-CG), Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD), Chronic kidney disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI)] were used to determine the burden of CKD with no race correction factor. Age- and sex-standardised prevalence rates were determined. Cohen Kappa and Spearman correlations were used to compare the estimators. Logistic regressions were applied to identify variables associated with prevalent CKD.
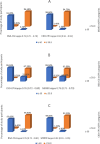
Results: Among 2 772 PLWH, the mean age was 38 years with males older than females (p < 0.001). The majority of participants were females (62.1%), married (54.8%), employed (85.7%), had underweight or normal body mass index (BMI) (62.2%), and were diagnosed with World Health Organization (WHO) clinical stages 1 and 2 (55.5%). The age- and sex-standardised prevalence of CKD ranged from 10.0 - 17.6% with the highest Spearman's correlation (0.928) observed with MDRD and CKD-EPI equations. Increasing age [AOR (95% CI), equation] was significantly associated with CKD across all equations [1.09 (1.06 - 1.13), BSA-CG; 1.07 (1.05 - 1.10), MDRD; 1.09 (1.06 -1.12), CKD-EPI]. Other variables associated with CKD [AOR (95% CI), equation] were anaemia [2.50 (1.34 - 4.68), BSA-CG; 1.73 (1.04 - 2.86), MDRD], BMI <25 kg/m2 [3.35 (1.55 - 7.26), BSA-CG; 2.02 (1.18 - 3.46), CKD-EPI], and CD4 counts ≤ 200 cells/µL [2.02 (1.06 - 3.87), BSA-CG].
Conclusion: There was a high prevalence of CKD among ART-naïve PLWH at enrollment, which highlights the need to evaluate this population for CKD. Aside increasing age and low CD4 counts, none of the traditional or HIV-specific risk factors were related to CKD diagnosis.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy naïve (ART-naive); Chronic kidney disease (CKD); HIV; People living with HIV (PLWH); Prevalence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS, UN Interagency Task force on NCDs. Responding to the Challenge of NonCommunicable diseases. 2019.
-
- Bertoldi A, De Crignis E, Miserocchi A, Bon I, Musumeci G, Longo S, et al. HIV and kidney: A dangerous liaison. New Microbiologica. 2017;40:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

