Current clinical practice and physicians' insights on Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer habouring epidermal growth factor receptor 20 insertion mutation
- PMID: 39179992
- PMCID: PMC11342509
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12797-3
Current clinical practice and physicians' insights on Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer habouring epidermal growth factor receptor 20 insertion mutation
Abstract
Background: The present study aimed to investigate physicians' perspectives on the diagnosis and treatment decisions for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion (exon20ins) mutations in a real-world setting in China using an online questionnaire.
Methods: This study was performed via the CAPTRA-Lung collaboration between December 9, 2022 and March 6, 2023. The questionnaire was distributed digitally to physicians around China and was comprised of three sections: basic characteristics of surveyed physicians, diagnosis and treatment status of NSCLC patients with the EGFR exon20ins-mutation, and physicians' perspectives on treatment options. Physicians who treat more than 10 patients with advanced NSCLC every month and who have treated patients with advanced EGFR exon20ins-mutant NSCLC in the past six months were involved in this study.
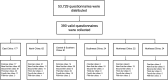
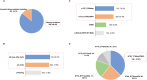
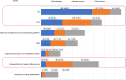
Results: A total of 53,729 questionnaires were distributed and 390 valid ones were collected. The EGFR mutation test was performed in 80.9% and 59.9% of patients receiving first-line or second-line therapy and beyond (hereinafter "second-line")therapy, respectively. In terms of treatment options, chemotherapy plus antiangiogenic therapy was the most common treatment option (30.0% of patients in first-line settings; 25.0% of patients in second-line settings), and a certain proportion of patients received novel EGFR exon20ins-targeted agents (including tyrosine kinase inhibitors [TKIs] and bispecific antibodies) in first- or second-line settings, which accounted for 11.9% and 15.7% of all treated patients, respectively. Additionally, physicians reported the highest satisfaction score for the efficacy and safety of targeted agents. Most physicians believed that EGFR exon20ins-targeted TKIs represented the most promising treatment option (80.2% in first-line treatment and 73.3% in second-line treatment). Among several novel agents under study, sunvozertinib has received the highest recognition for efficacy and safety.
Conclusions: This study investigated the current diagnosis and treatment status and physicians' perspective, of patients with EGFR exon20ins-mutant NSCLC. The results highlight significant unmet clinical needs in this subgroup of patients. EGFR exon20ins-targeted TKIs were recognized as the most promising treatment regimen and may benefit more patients considering their awareness and acceptance of targeted therapy.
Keywords: EGFR exon20ins; Questionnaire; Real-world clinical practice; Targeted agents.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global Cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rabe KF. Precision diagnosis and treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):849–61. - PubMed
-
- Imyanitov EN, Iyevleva AG, Levchenko EV. Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current status and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021;157:103194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

