Outcomes from low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39180592
- PMCID: PMC11457553
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-024-07473-w
Outcomes from low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The current standard of treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is surgery with or without adjuvant radiotherapy. With a growing debate about overdiagnosis and overtreatment of low-risk DCIS, active surveillance is being explored in several ongoing trials. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the recurrence of low-risk DCIS under various treatment approaches.
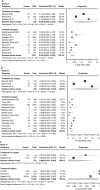
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane were searched for studies reporting ipsilateral breast tumour event (IBTE), contralateral breast cancer (CBC), and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) rates at 5 and 10 years in low-risk DCIS. The primary outcome was invasive IBTE (iIBTE) defined as invasive progression in the ipsilateral breast.
Results: Thirty three eligible studies were identified, involving 47,696 women with low-risk DCIS. The pooled 5-year and 10-year iIBTE rates were 3.3% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.3, 8.1) and 5.9% (95% CI: 3.8, 9.0), respectively. The iIBTE rates were significantly lower in patients who underwent surgery compared to those who did not, at 5 years (3.5% vs. 9.0%, P = 0.003) and 10 years (6.4% vs. 22.7%, P = 0.008). Similarly, the 10-year BCSS rate was higher in the surgery group (96.0% vs. 99.6%, P = 0.010). In patients treated with breast-conserving surgery, additional radiotherapy significantly reduced IBTE risk, but not total-CBC risk.
Conclusion: This review showed a lower risk of progression and better survival in women who received surgery and additional RT for low-risk DCIS. However, our findings were primarily based on observational studies, and should be confirmed with the results from the ongoing trials.
Keywords: Ductal carcinoma in situ; Low-risk DCIS; Outcomes; Radiotherapy; Surgery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gangnon RE, Sprague BL, Stout NK, Alagoz O, Weedon-Fekjaer H et al (2015) The contribution of mammography screening to breast cancer incidence trends in the United States: an updated age-period-cohort model. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 24:905–912. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-1286 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical