Removal of oxytetracycline from pharmaceutical wastewater using kappa carrageenan hydrogel
- PMID: 39181917
- PMCID: PMC11344773
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69989-x
Removal of oxytetracycline from pharmaceutical wastewater using kappa carrageenan hydrogel
Abstract
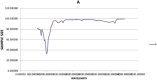
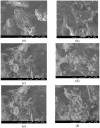
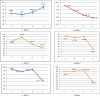
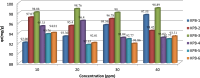
This study investigated the adsorption of Oxytetracycline (OTC) from pharmaceutical wastewater using a kappa carrageenan based hydrogel (KPB). The aim of the present study was to explore the potential of KPB for long-term pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. A sustainable adsorbent was developed to address oxytetracycline (OTC) contamination. The hydrogel's structural and adsorption characteristics were examined using various techniques like Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), and kinetic models. The results revealed considerable changes in the vibrational modes and adsorption bands of the hydrogel, suggesting the effective functionalization of Bentonite nano-clay. Kappa carrageenan based hydrogel achieved the maximum removal (98.5%) of OTC at concerntration of 40 mg/L, pH 8, cotact time of 140 min and adsorbent dose of 0.1 g (KPB-3). Adsorption of OTC increased up to 99% with increasing initial concentrations. The study achieved 95% adsorption capacity for OTC using a KPB film at a concentration of 20 mg/L and a 0.1 g adsorbent dose within 60 min. It also revealed that chemisorptions processes outperform physical adsorption. The Pseudo-Second-Order model, which emphasized the importance of chemical adsorption in the removal process, is better suited to represent the adsorption behavior. Excellent matches were found that R2 = 0.99 for KPB-3, R2 = 0.984 for KPB-2 and R2 = 0.989 for KPB-1 indicated strong chemical bonding interactions. Statisctical analysis (ANOVA) was performed using SPSS (version 25) and it was found that pH and concentration had significant influence on OTC adsorption by the hydrogel, with p-values less than 0.05. The study identified that a Kappa carrageenan-based hydrogel with bentonite nano-clay and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) can efficiently remove OTC from pharmaceutical effluent, with a p-value of 0.054, but weak positive linear associations with pH, temperature, and contact time. This research contributed to sustainable wastewater treatment and environmental engineering.
Keywords: Bentonite nano-clay; Hydrogel; Kappa Carrageenan; Oxytetracycline; Pharmaceutical wastewater.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Wang, T., Jiang, M., Yu, X., Niu, N. & Chen, L. Application of lignin adsorbent in wastewater Treatment: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol.302, 122116. 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122116 (2022).10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122116 - DOI
-
- Das, P. P., Sharma, M. & Purkait, M. K. Recent progress on electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol.292, 121058. 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121058 (2022).10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121058 - DOI
-
- Irshad, M. A. et al. Application of nanomaterials for cadmium adsorption for sustainable treatment of wastewater: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut.234(1), 54 (2023).10.1007/s11270-023-06064-7 - DOI
-
- Li, Y., Dong, X. & Zhao, L. Application of magnetic chitosan nanocomposites modified by graphene oxide and polyethyleneimine for removal of toxic heavy metals and dyes from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.192, 118–125. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.202 (2021). 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.202 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

