A scoping review of large language model based approaches for information extraction from radiology reports
- PMID: 39182008
- PMCID: PMC11344824
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01219-0
A scoping review of large language model based approaches for information extraction from radiology reports
Abstract
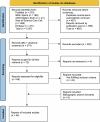
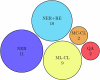
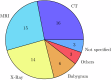
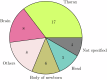
Radiological imaging is a globally prevalent diagnostic method, yet the free text contained in radiology reports is not frequently used for secondary purposes. Natural Language Processing can provide structured data retrieved from these reports. This paper provides a summary of the current state of research on Large Language Model (LLM) based approaches for information extraction (IE) from radiology reports. We conduct a scoping review that follows the PRISMA-ScR guideline. Queries of five databases were conducted on August 1st 2023. Among the 34 studies that met inclusion criteria, only pre-transformer and encoder-based models are described. External validation shows a general performance decrease, although LLMs might improve generalizability of IE approaches. Reports related to CT and MRI examinations, as well as thoracic reports, prevail. Most common challenges reported are missing validation on external data and augmentation of the described methods. Different reporting granularities affect the comparability and transparency of approaches.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jurafsky, D. & Martin, J. H. Speech and Language Processing. An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, and Speech Recognition (Pearson Education, 2024).
-
- Birhane, A., Kasirzadeh, A., Leslie, D. & Wachter, S. Science in the age of large language models. Nat. Rev. Phys.5, 277–280 (2023). 10.1038/s42254-023-00581-4 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

