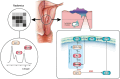
Endometrial cancer risk stratification using MRI radiomics: corroborating with choline metabolism
- PMID: 39182135
- PMCID: PMC11344325
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-024-00756-x
Endometrial cancer risk stratification using MRI radiomics: corroborating with choline metabolism
Abstract
Background and purpose: Radiomics offers little explainability. This study aims to develop a radiomics model (Rad-Score) using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) to predict high-risk patients for nodal metastasis or recurrence in endometrial cancer (EC) and corroborate with choline metabolism.
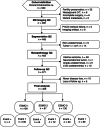
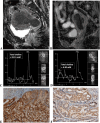
Materials and methods: From August 2015 to July 2018, 356 EC patients were enrolled. Rad-Score was developed using LASSO regression in a training cohort (n = 287) and validated in an independent test cohort (n = 69). MR spectroscopy (MRS) was also used in 230 patients. Nuclear MRS measured choline metabolites in 70 tissue samples. The performance was compared against European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) risk groups. A P < .05 denoted statistical significance.
Results: Rad-Score achieved 71.1% accuracy in the training and 71.0% in the testing cohorts. Incorporating clinical parameters of age, tumor type, size, and grade, Rad-Signature reached accuracies of 73.2% in training and 75.4% in testing cohorts, closely matching the performance to the post-operatively based ESMO's 70.7% and 78.3%. Rad-Score was significantly associated with increased total choline levels on MRS (P = .034) and tissue levels (P = .019).
Conclusions: Development of a preoperative radiomics risk score, comparable to ESMO clinical standard and associated with altered choline metabolism, shows translational relevance for radiomics in high-risk EC patients.
Trial registration: This study was registered in ClinicalTrials.gov on 2015-08-01 with Identifier NCT02528864.
Keywords: Diagnostic accuracy; Diffusion-weighted imaging; Endometrial carcinoma; Magnetic resonance imaging; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical