Loss of mitochondria long-chain fatty acid oxidation impairs skeletal muscle contractility by disrupting myofibril structure and calcium homeostasis
- PMID: 39182841
- PMCID: PMC11408158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102015
Loss of mitochondria long-chain fatty acid oxidation impairs skeletal muscle contractility by disrupting myofibril structure and calcium homeostasis
Abstract
Objective: Abnormal lipid metabolism in mammalian tissues can be highly deleterious, leading to organ failure. Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 2 (CPT2) deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder affecting the liver, heart, and skeletal muscle due to impaired mitochondrial oxidation of long-chain fatty acids (mLCFAO) for energy production.
Methods: However, the basis of tissue damage in mLCFAO disorders is not fully understood. Mice lacking CPT2 in skeletal muscle (Cpt2Sk-/-) were generated to investigate the nexus between mFAO deficiency and myopathy.
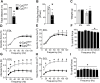
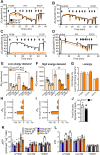
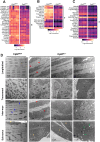
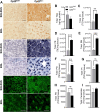
Results: Compared to controls, ex-vivo contractile force was reduced by 70% in Cpt2Sk-/- oxidative soleus muscle despite the preserved capacity to couple ATP synthesis to mitochondrial respiration on alternative substrates to long-chain fatty acids. Increased mitochondrial biogenesis, lipid accumulation, and the downregulation of 80% of dystrophin-related and contraction-related proteins severely compromised the structure and function of Cpt2Sk-/- soleus. CPT2 deficiency affected oxidative muscles more than glycolytic ones. Exposing isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum to long-chain acylcarnitines (LCACs) inhibited calcium uptake. In agreement, Cpt2Sk-/- soleus had decreased calcium uptake and significant accumulation of palmitoyl-carnitine, suggesting that LCACs and calcium dyshomeostasis are linked in skeletal muscle.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that loss of CPT2 and mLCFAO compromise muscle structure and function due to excessive mitochondrial biogenesis, downregulation of the contractile proteome, and disruption of calcium homeostasis.
Keywords: CPT2; Calcium; Fatty acid oxidation; Muscle contraction; Palmitoyl-carnitine.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

